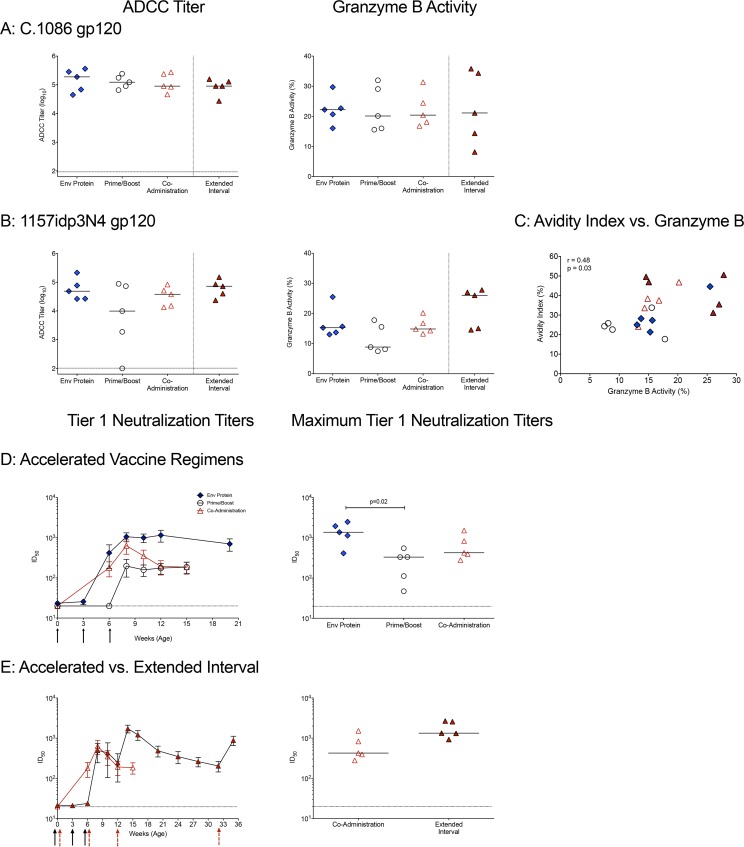
FIG 5.
ADCC activity and tier 1 neutralizing antibodies in plasma. (A) Plasma was tested for the ability to mediate ADCC against cells coated with the C.1086 gp120 immunogen. Shown are the log10 reciprocal endpoint titers of plasma with detectable ADCC activity for each animal in the four vaccine groups. The horizontal dashed line represents the cutoff for positivity. Plasma samples from the extended-interval group at week 14 or from the accelerated vaccine regimen groups at week 8 were tested. The granzyme B activity against C.1086 gp120 cells is expressed as the proportion of target cells positive for proteolytically active granzyme B out of the total viable target cell population after subtracting the background activity observed in wells containing effector and target cells in the absence of plasma. (B) The ADCC activities against target cells expressing the heterologous clade C SHIV 1157ipd3N4 gp120 are shown. (C) Spearman's rank correlations between the C.1086 gp120 IgG avidity indices and granzyme B activities against SHIV1157ipd3N4 gp120. (D) Development of plasma IgG that neutralize clade C MW965 infection of TZM-bl cells by 50%. Shown are mean 50% inhibitory concentrations (IC50s) ± SD for each of the vaccine groups (left) and peak IC50 titers of neutralizing plasma antibodies (right) in animals of the accelerated vaccine groups. (E) Comparison of the kinetics and peak IC50 titers of neutralizing plasma antibodies between the accelerated and extended-interval coadministration vaccine regimens. The symbols are as defined in the keys in Fig. 2A and 3A.