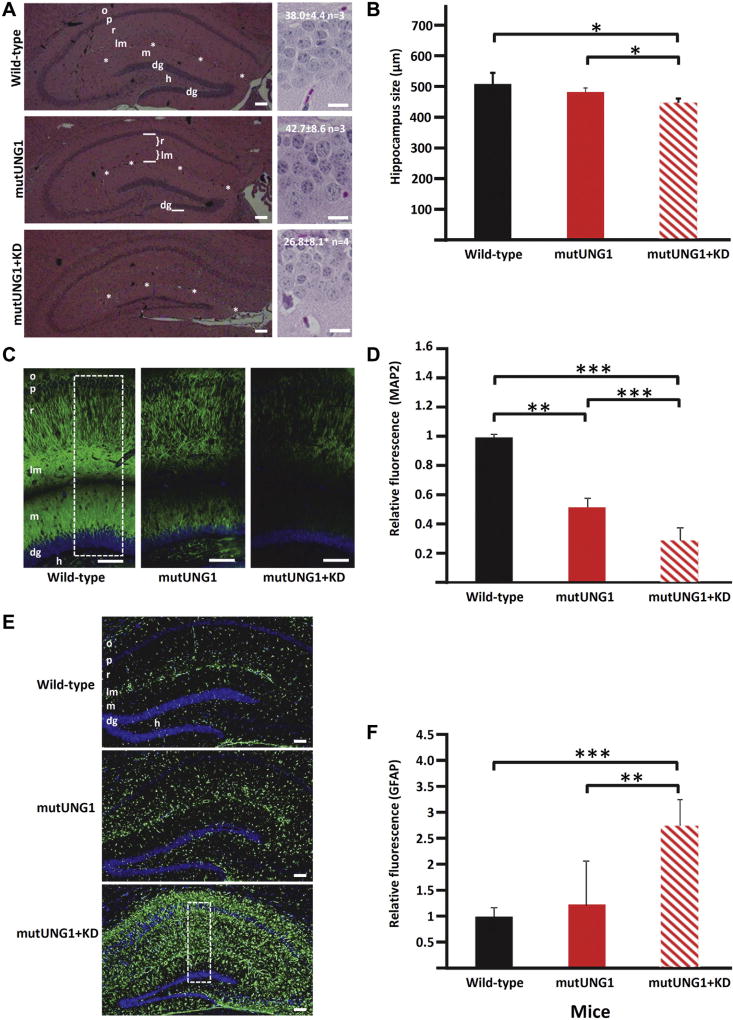
Fig. 2.
A ketogenic diet accelerates atrophy, neurodegeneration, and reactive astrogliosis in the hippocampus in mutUNG1-expressing mice. (A) Representative HE-stained coronal paraffin sections of hippocampus illustrate increased atrophy and neuronal degeneration in mutUNG1-expressing mice fed a ketogenic diet (KD, bottom panels) compared with wild-type (top panels) and mutUNG1-expressing mice fed a standard diet (middle panel). Numbers of cells were counted in a 100-µm long stretch of the infrapyramidal part of the granular cell layer (dg, marked in the middle left panel) on pictures scanned at high magnification. Samples pictures are shown in right panels together with results (mean ± standard deviation, n mice, p = 0.05 for difference between the lower 2). (B) Quantification of the thickness of hippocampal layers r + lm (in coronal sections, A, marked in the middle frame) shows a significant decrease in hippocampus size in mutUNG1-expressing mice fed a ketogenic diet compared with wild-type and mutUNG1-expressing mice fed a standard diet, respectively, (n = 3 mice per group, p = 0.02 and p = 0.03). (C) Coronal paraffin-embedded sections of hippocampus immunolabeled for the neuronal marker MAP2 in wild-type and mutUNG1-expressing mice fed a standard diet, and mutUNG1-expressing mice fed a ketogenic diet, the latter showing loss of labeled pyramidal and granule cell dendrites. (D) Quantification of immunostaining shows a significant decrease of MAP2 in mutUNG1-expressing mice fed a ketogenic diet compared with wild-type and mutUNG1-expressing mice fed a standard diet (n = 3 mice per group, p < 0.0001 and p < 0.0001); mutUNG1-expressing mice fed a standard diet also differed from wild-type mice (p = 0.01). (E) Coronal paraffin-embedded sections of hippocampus immunostained for the astrocyte marker GFAP in wild-type and mutUNG1-expressing mice fed a standard diet, and mutUNG1-expressing mice fed a ketogenic diet. (F) Quantification of immunofluorescence shows a significant increase of GFAP in mutUNG1-expressing mice fed a ketogenic diet compared with wild-type and mutUNG1-expressing mice fed a standard diet (n = 3 mice per group, p = 0.003, p < 0.0001). Stippled rectangles in (C) and (E) indicate regions of interest used for quantification of immunoreactivity. Scale bars = 100 µm (C and E) and 20 µm (right panels in A). Asterisk series marks fissura hippocampi between lm and m. In this and subsequent figures, levels of statistical significance are indicated by asterisks (*p≤ 0.05; **p≤ 0.01; ***p≤ 0.001). Abbreviations: dg, granule cell layer of dentate gyrus; h, hilus of the dentate gyrus; HE, hematoxylin and eosin; lm, stratum lacunosum-moleculare of hippocampus CA1; m, stratum moleculare of dentate gyrus; o, stratum oriens; p, pyramidal cell layer; r, stratum radiatum.