Figure 1.
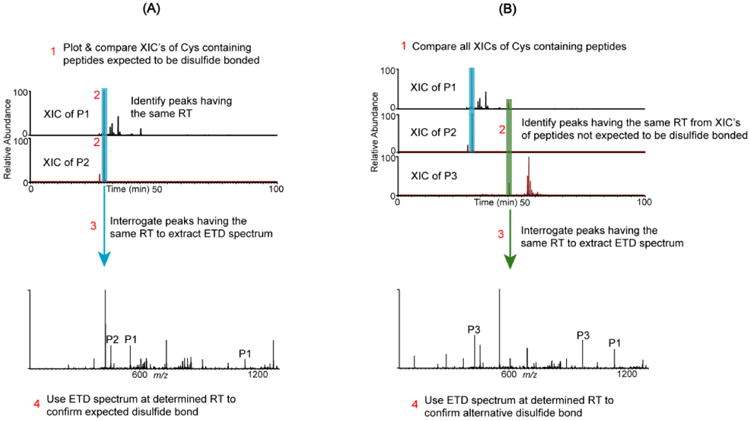
Schematic representation of the disulfide mapping approach for expected and alternative disulfides. (A) Assignment of an expected disulfide bond between Cys-containing peptides P1 and P2. Step 1: Plot XIC's for each peptide. Step 2: Identify peaks with the same retention time. Step 3: Extract the corresponding ETD spectrum, which confirms the disulfide bond. Step 4: Verify that marker ions of each chain (P1 & P2 peaks) and c and z ions from both chains are present in the ETD spectrum. (B) Alternative disulfide bonds are verified by the following: Step 1: Plot and compare the XIC's of all Cys-containing peptides. Step 2: If peaks with the same RT are identified in the XIC's of peptides that are not expected to be disulfide bonded, then steps 3 and 4 in (A) are used to verify whether the two peptides are bonded by an alternative disulfide bond.
