Figure 2.
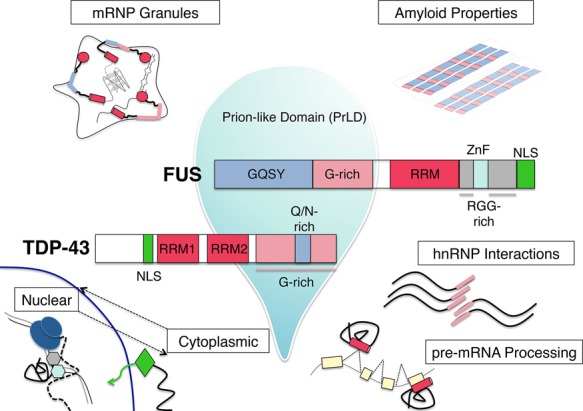
Functional domains of the RBPs TDP-43 and FUS and their cellular roles. Domain architecture of the disease-related proteins TDP-43 and FUS, with emphasis on the prion-like domains (PrLDs) that contribute to liquid–liquid phase separation, represented by a liquid droplet. Various cellular roles of these proteins, including nuclear–cytoplasmic shuttling, pre-mRNA processing, hnRNP interactions, mRNP granule formation, and amyloid-like fibrillization, are diagrammed, with the domains implicated in these processes highlighted.
