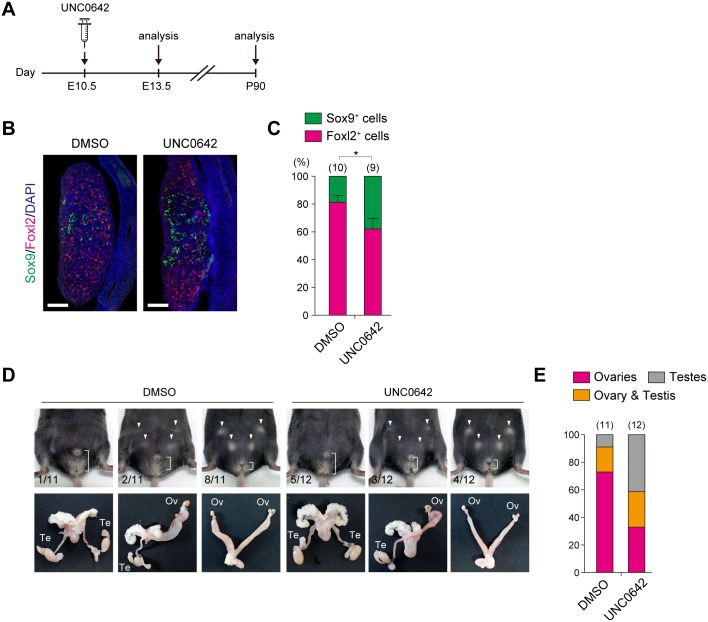
Fig 8. Embryonic administration of the GLP/G9a inhibitor UNC0642 rescues aberrant sex development of Jmjd1a-deficient mice.
(A) Experimental scheme of UNC0642 treatment. 0.5 mg of UNC0642 was intraperitoneally injected into pregnant females carrying E10.5 Jmjd1a-deficient embryos, and the subsequent gonadal differentiation of E13.5 embryos (B) and 3-months-old adults (D) was examined. (B) Immunofluorescence analysis of sex differentiation of E13.5 embryonic gonads using antibodies against Sox9 and Foxl2. Scale bar, 200 μm. (C) Quantification of Sox9- and Foxl2-positive cells in E13.5 gonads. Numbers of embryos examined are shown above the bars. Data are presented as mean ± SD. * P < 0.05. (D) External genitalia (upper) and gonads and genital tracts (lower) of UNC0642-treated (right) and solvent-treated (left) XY Jmjd1a-deficient animals. Arrowheads represent mammary glands. The distance between anus and penis or vagina is indicated. Frequencies are presented in the lower left corner. Te, testis; Ov, ovary. (E) Frequency analysis of abnormal sex differentiation of 3-months-old mice, determined by examining the internal genitalia. Numbers of animals examined are shown above the bars.