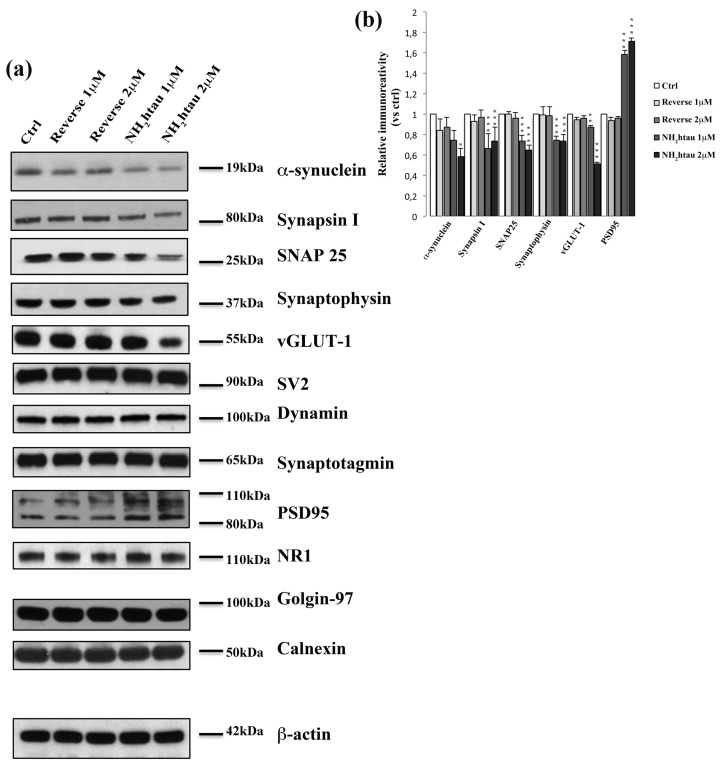
Figure 5. Long-term application of NH2htau induces a marked and selective loss of exocytotic presynaptic vesicles proteins in cultured hippocampal neurons.
a.-b. Western blotting analysis (n=12) was carried out on equal amounts of total protein extract (40µg) from mature hippocampal primary neurons (DIV15) exposed for 48h to increasing subtoxic concentration (1-2µM) of NH2htau and its reverse control sequence. Immunoblots (a) were probed with antibodies against several presynaptic- (α-synuclein, synapsin I, synaptosomal-associated protein 25 SNAP-25, synaptophysin, vesicular glutamate transporter 1 vGLUT1 , synaptic vesicle protein 2 SV2, dynamin, synaptotagmin) and post-synaptic markers (N-Methyl-D-aspartate NMDA Receptor Subunit NR1, postsynaptic density protein 95 PSD95) and against not-synaptic proteins located in trans-Golgi network and endoplasmic reticulum (golgin-97 and calnexin). Cropped representative WB are shown. Densitometric quantification of immunoreactivity levels (b) was calculated by normalizing the values on the β-actin intensity and expressed as ratio respect to corresponding ctrl values.Values are means of at least nine independent experiments and statistically significant differences were calculated by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-hoc test (*p < 0,05; **p<0,01; ***p<0,0001 versus untreated ctrl).