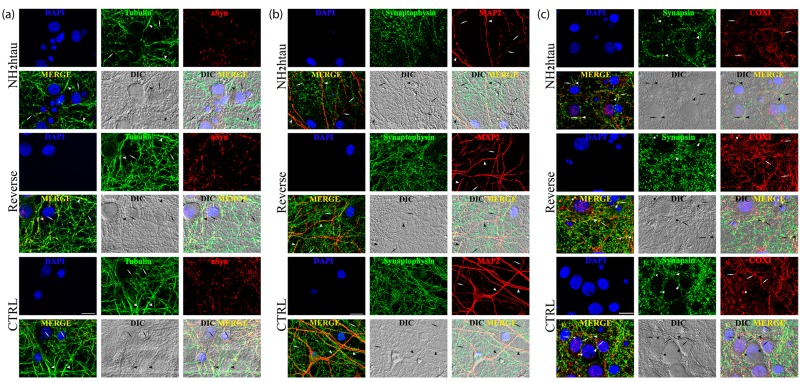
Figure 6. Distortion of the dendritic tree, microtubule breakdown and mitochondria loss occur in concomitance with decline of presynaptic proteins density in living hippocampal neurons chronically exposed to NH2htau.
a.-b.-c. Confocal microscopy analysis of double immunofluorescence carried out on mature hippocampal primary neurons (DIV15) exposed for 48h to NH2htau and its reverse control sequence (1µM). Merge images show the overlay of the three fluorescence channels, Differential Interference Contrast (DIC; gray channel) enables the visualization of the neuritic network, DIC Merge is the composition of the three fluorescence and of the DIC channels. (a): presynaptic synaptophysin (green channel) and dendritic MAP-2 (red channel). Nuclei (blue) were stained with Hoechst 33258 (0.5 mg/ml). Arrowheads and arrows point to MAP2- positive neurites of larger and smaller caliber, respectively. (b): presynaptic α-synuclein (green channel) and neuron-specific cytoskeletal beta III tubulin (red channel). Arrowheads and arrows point to beta III tubulin-positive neurites of larger and smaller caliber, respectively. (c): presynaptic synapsin I (green channel) and mitochondrial marker COX I (red channel). Arrowheads point to synapsin I-labeled presynaptic spots and arrows point to COX I -positive mitochondrial structures. In the merge, DIC and DIC-Merge channels, arrowheads and arrows appear in opposition to give evidence to mitochondria resident at juxstaposed presynaptic sites. Asterisks mark typical punctuate structures immunoreactive for both synapsin I and COX I (yellow dots) representing mitochondria which are localized to presynaptic sites (i.e.synaptic mitochondria). Note the loss of double-stained synapsin I/COX I puncta and the decrease of juxstaposed presynaptic sites/mitochondria in the NH2htau-treated cultures. Images are representative of at least three independent experiments. Scale bar: A=20 µm ;B-C=10 µm.