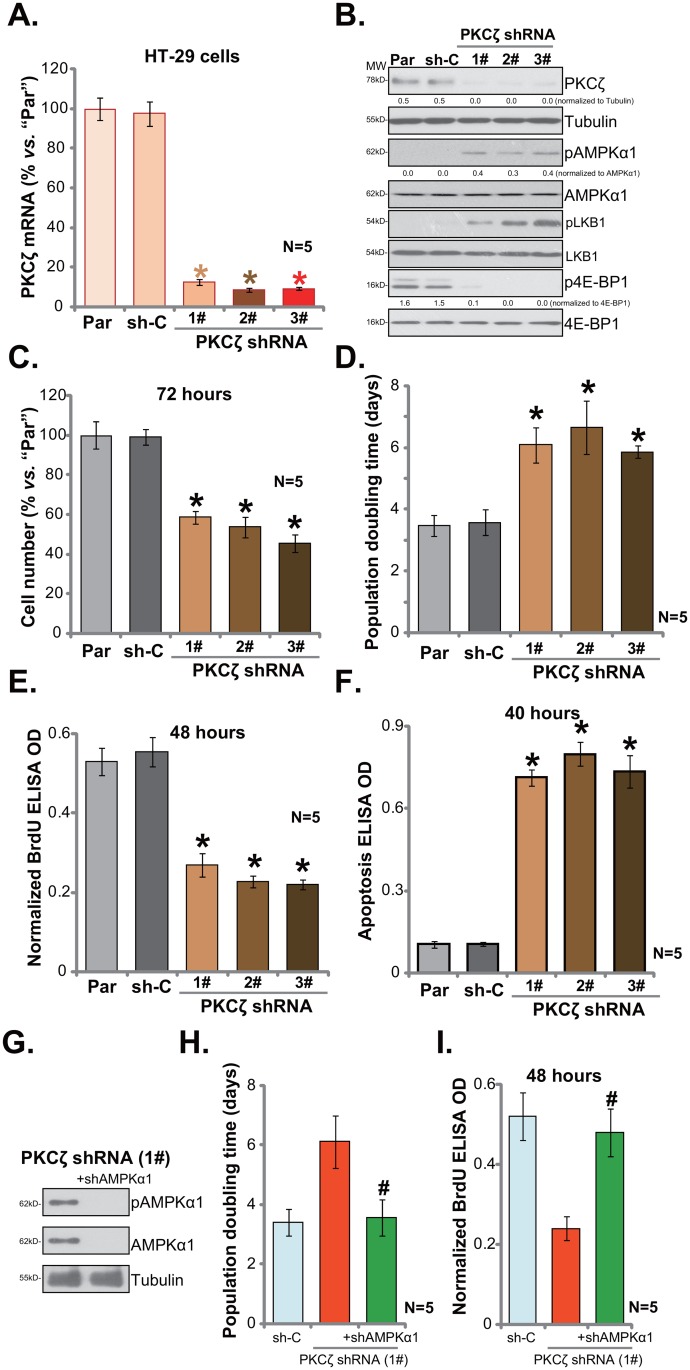
Figure 2. PKCζ shRNA knockdown activates AMPK and inhibits HT-29 cell proliferation.
Stable HT-29 cells, expressing listed PKCζ-targeting shRNA (“1#/2#/3#”), or non-sense shRNA control (“sh-C”), as well as the parental control HT-29 cells (“Par”) were subjected to qRT-PCR (A) assay and Western blotting assay (B) of listed genes; proliferation of above cells was tested by viable cell counting assay (C), population doubling time was calculated in (D) and BrdU ELISA assay (E); cell apoptosis was quantified via the Histone DNA ELISA assay (F). PKCζ-targeting shRNA (“1#”)-expressing HT-29 cells were further infected with lentiviral AMPKα1 shRNA (“+shAMPKα1”), expressions of listed proteins were shown (G); population doubling time (H) and BrdU ELISA OD (I) were also shown. For the proliferation and apoptosis assays, exact same number of viable cells (“trypan blue negative”) of different background was plated initially (Same for all Figures). Band intensity was quantified (B). * p <0.05 vs. “sh-C”. # p <0.05 vs. “PKCζ shRNA (1#)” only group. Experiments in this figure were repeated five times, and similar results were obtained each time.