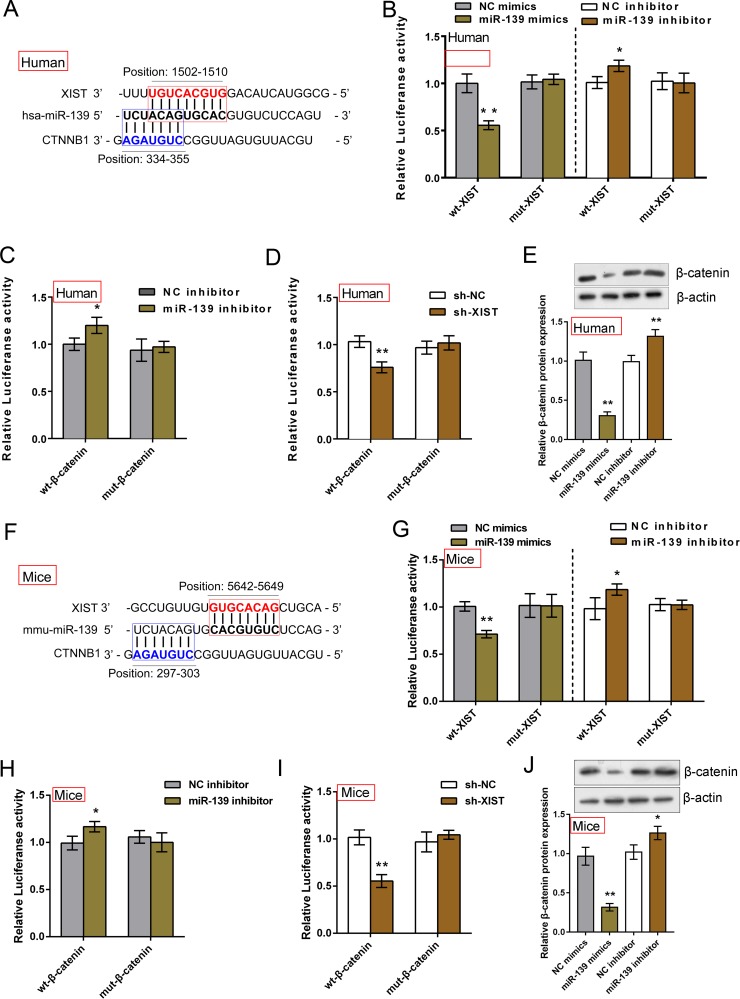
Figure 4. XIST competed with β-catenin for miR-139 binding in IMR-90 and MLFCs.
(A) and (F) Online tools predicted that XIST and β-catenin shared an almost identical binding site of miR-139. A wt-XIST luciferase reporter gene vector (human or mice), a mut-XIST vector containing a 7 bp (human) or a 6 bp (mice) mutation on putative binding site of miR-139, a wt-β-catenin vector (human or mice), a mut-β-catenin vector containing a 5 bp mutation on putative binding site of miR-139 (human or mice) was constructed. (B) The indicated XIST vectors (human) were co-introduced into IMR-90 cells with miR-139 mimics or miR-139 inhibitor; the luciferase activity was determined by using dual luciferase assays. (C) The indicated β-catenin vectors (human) were co-introduced into IMR-90 cells with miR-139 inhibitor; the luciferase activity was determined by using dual luciferase assays. (D) The indicated β-catenin vectors (human) were co-introduced into IMR-90 cells with sh-XIST; the luciferase activity was determined by using dual luciferase assays. (E) The protein levels of β-catenin in miR-139 mimics- or miR-139 inhibitor-transfected IMR-90 cells were evaluated using Western blot assays. (G) The indicated XIST vectors (mice) were co-introduced into MLFCs with miR-139 mimics or miR-139 inhibitor; the luciferase activity was determined by using dual luciferase assays. (H) The indicated β-catenin vectors (mice) were co-introduced into MLFCs with miR-139 inhibitor; the luciferase activity was determined by using dual luciferase assays. (I) The indicated β-catenin vectors (mice) were co-introduced into MLFCs with sh-XIST; the luciferase activity was determined by using dual luciferase assays. (J) The protein levels of β-catenin in miR-139 mimics- or miR-139 inhibitor-transfected MLFCs were evaluated using Western blot assays. The data are showed as mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.