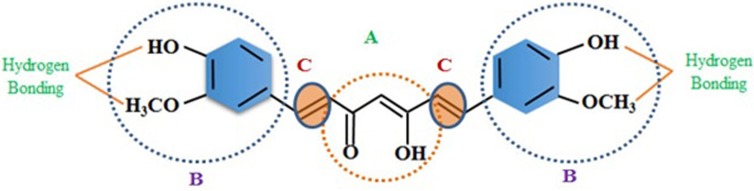
Figure 2. Structure of Curcumin.
(A) b-diketone or keto-enol; (B) phenolic; (C) alkene linker. Curcumin contains three chemical entities in its structure: two aromatic ring systems containing o-methoxy phenolic groups, connected by a seven carbon linker consisting of an α, β-unsaturated β-diketone moiety.