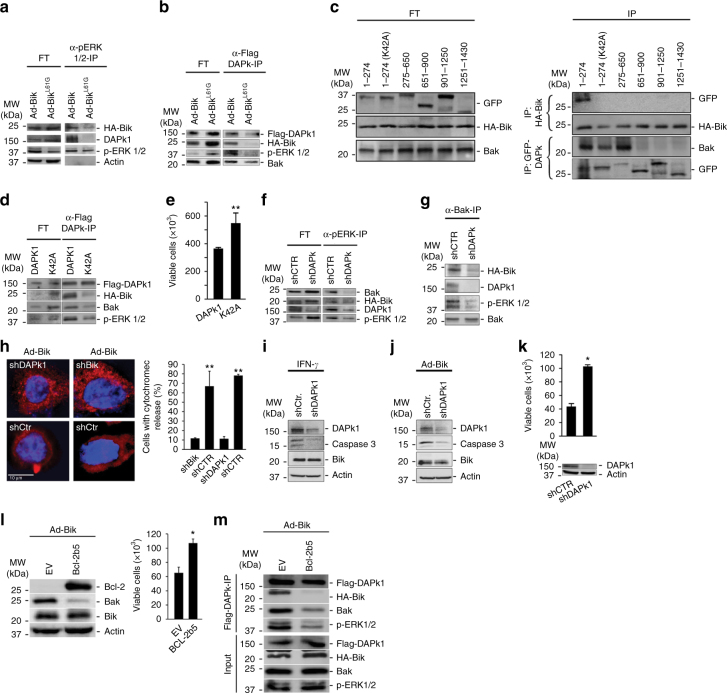
Fig. 3.
DAPk1 facilitates Bik-induced cell death by forming a complex with Bik, ERK1/2 and Bak. a Protein lysates from HAECs 24 h after infection with HA-Ad-Bik or HA-Ad-BikL61G were immunoprecipitated with anti-pERK1/2 antibodies. The flow through (FT) and the immunoprecipitates (IPs) were probed with antibodies to HA, DAPK1, p-ERK1/2, and ERK1/2 by western blotting. b 293T cells were transfected with Flag-DAPk1 and 48 h later infected with 100 MOI HA-Ad-Bik or HA-Ad-BikL61G. After 24 h, protein lysates were immunoprecipitated with α-Flag antibodies and the FT and IP were probed for activated Bak, HA, and ERK1/2 by western blotting. c 293T cells transfected with various GFP-tagged DAPk1 deletions constructs, infected with HA-Ad-Bik, and subjected to immunoprecipitation using anti-HA or anti-GFP antibodies. The flow through (FT) and the IPs were probed for GFP, HA, activated Bak. d Mutation of Lys42 in the kinase domain of DAPk1 diminishes Bik–Bak–DAPk1–ERK1/2 interaction. 293T cells were transfected with Flag-DAPk1 or Flag-DAPK1K42A and 48 h later infected with 100 MOI HA-Ad-Bik. Protein lysates were immunoprecipitated using α-Flag antibodies and the FT and IP were probed for Flag, HA, Bak, and ERK1/2 by western blotting. e Cell viability of 293T cells transfected with Flag-DAPk1 or Flag-DAPK1K42A was analyzed by trypan blue assay. f, g Knockdown of DAPk1 suppresses the interaction between Bak, Bik, and ERK1/2. Protein lysates from HAECs stably expressing shCtr or shDAPk1 were infected with HA-Ad-Bik and immunoprecipitated using anti-pERK1/2 f or anti-active Bak (Ab1) g antibodies. The FT and IPs were probed for activated Bak, HA, DAPk1, and p-ERK1/2 by western blotting. h HAECs stably expressing shCtr or shDAPk1 were infected with 100 MOI of Ad-Bik in the presence of 20 µM pan-caspase inhibitor Q-VD-Oph for 18 h, fixed and stained for cytochrome c, and the percentage of cells with cytochrome c release was analyzed by fluorescent microscopy. i, j Cell lysates from HAECs stably expressing shCtr or shDAPk1 and treated with 50 ng/ml IFN-γ i or 100 MOI Ad-Bik j were analyzed for cleaved caspase 3 by immunoblotting. k HAECs stably expressing shCtr or shDAPk1 were analyzed for knockdown of DAPk1 by western blotting. Cell viability was determined by trypan blue exclusion assay 24 h after infection with100 MOI Ad-Bik. l 293T cells were transfected with plasmids expressing empty vector (EV) or ER-targeted Bcl-2 (Bcl-2b5). Forty-eight hours later, cells were infected with 100 MOI Ad-Bik and protein lysates were analyzed for the expression of Bcl-2, Bak, and Bik. Cell viability was determined by trypan blue exclusion. m 293T cells were transfected with plasmids expressing empty vector or Bcl-2b5 together with plasmids expressing Flag-DAPk1 and 48 h later infected with 100 MOI HA-Ad-Bik. Protein lysates were immunoprecipitated using α-Flag antibodies and the FT and IP were probed for Flag-DAPk1, HA-Bik, Bak and ERK1/2 by western blotting. Differences between two groups were assessed for significance by Student’s t test. ANOVA was used to perform pair-wise comparison of the data from more than two groups followed by Fisher least significant difference test. Error bars indicate ± SEM, n = 5; * = P < 0.05, ** = P < 0.01