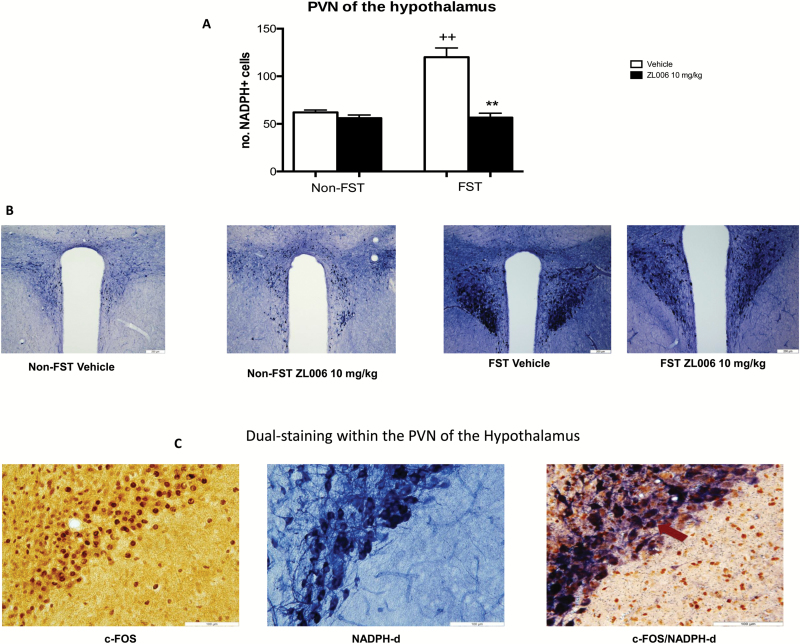
Figure 3.
Effect of 4-((3,5-dichloro-2-hydroxybenzyl)amino)-2-hydroxybenzoic acid (ZL006) administration on NADPH-d histochemistry in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus (PVN) of the hypothalamus of FST-exposed animals. Animals were subjected to a 15-minute pre-FST swim session or handled. At 1 hour following the pretest, animals were administered vehicle (i.p.) or ZL006 (10 mg/kg; i.p.). A second and a third injection were administered 5 hours and 1 hour prior to the 5-minute FST test session on the following day. Non-FST were handled at this time. Treatment with ZL006 attenuated FST-induced NADPH-d staining in the PVN of the hypothalamus (Figure 3A). Data expressed as mean and SEM (n=4–6). +P<.05 relative to non-FST vehicle-treated group. ++P<.01 relative to non-FST vehicle-treated group. **P<.01 relative to corresponding FST vehicle-treated group. Representative photomicrographs of PVN sections stained for NADPH-d from the treatment groups Vehicle Non FST; ZL006 Non FST; Vehicle FST; ZL006 FST are shown in 3B. Representative photomicrographs of dual staining for c-FOS and NADPH-d depicting colocalization within the PVN from the Vehicle FST treatment group is shown in 3C.