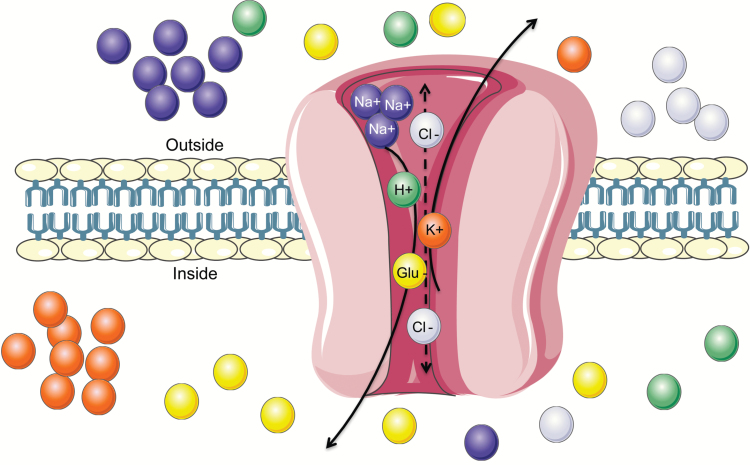
Figure 1.
Diagram of a glutamate transporter. The transport of glutamate is coupled with cotransport of 3 sodium (Na+), 1 hydrogen (H+), and 1 potassium (K+) ion along their concentration gradient. The stoichiometry of coupling has been determined for excitatory amino acid transporter (EAAT)1–4; however, the order of ion binding is not completely resolved. EAATs 1–3 compared with EAAT4 transport glutamate with considerably different kinetics and voltage dependence despite a similar uptake mechanism. Additionally, EAATs perform an uncoupled flux of chloride (Cl-) cations. This latter function is most predominant in EAAT4 and EAAT5, and nearly absent in EAAT2.