Fig. 4.
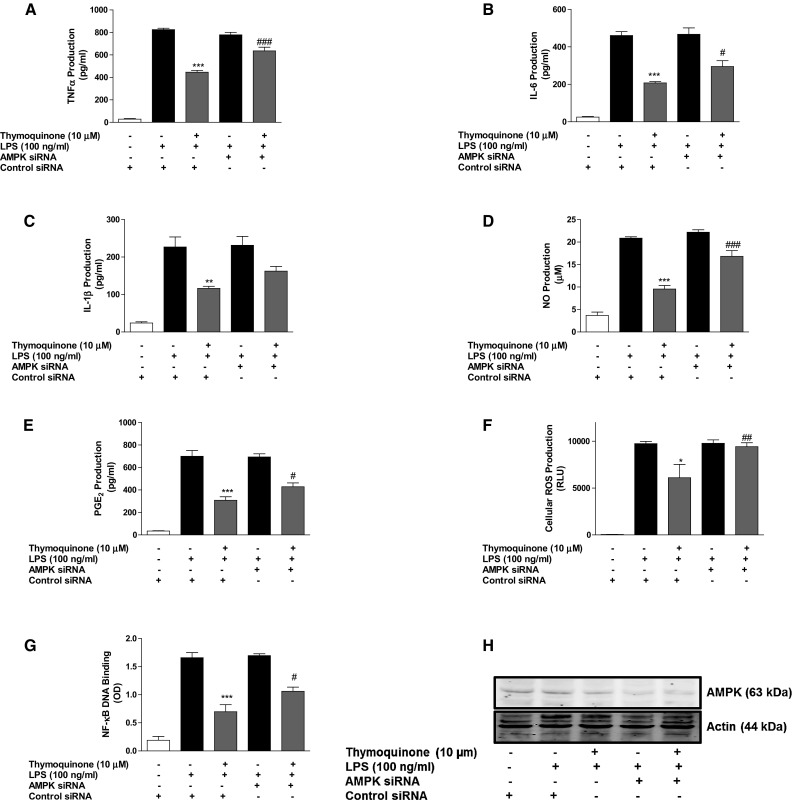
Inhibition of neuroinflammation by thymoquinone is dependent on AMPKα. Control siRNA- and AMPKα siRNA-transfected BV2 cells were pre-treated with thymoquinone (10 μM) prior to stimulation with LPS (100 ng/ml) for 24 h. Cells were analysed for TNFα (a), IL-6 (b), IL-1β (c), nitrite (d) PGE2 (e) and ROS (f). In g nuclear extracts from cells were added to 96-well plates to which an oligonucleotide containing the NF-κB consensus site (5′-GGGACTTTCC-3′) has been immobilised, followed by addition of NF-κB and HRP-conjugated antibodies. Absorbance was read in a microplate reader. Western blot experiments on cell extracts to determine knockout efficiency (h). (Mean ± SEM; **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 thymoquinone + LPS treatment compared with LPS alone in control siRNA-transfected cells; # p < 0.05, ### p < 0.001, thymoquinone + LPS treatment in AMPK siRNA-transfected cells compared with thymoquinone + LPS treatment in control siRNA-transfected cells; one-way ANOVA with ANOVA post hoc Student Newman–Keuls test)
