Fig. 6.
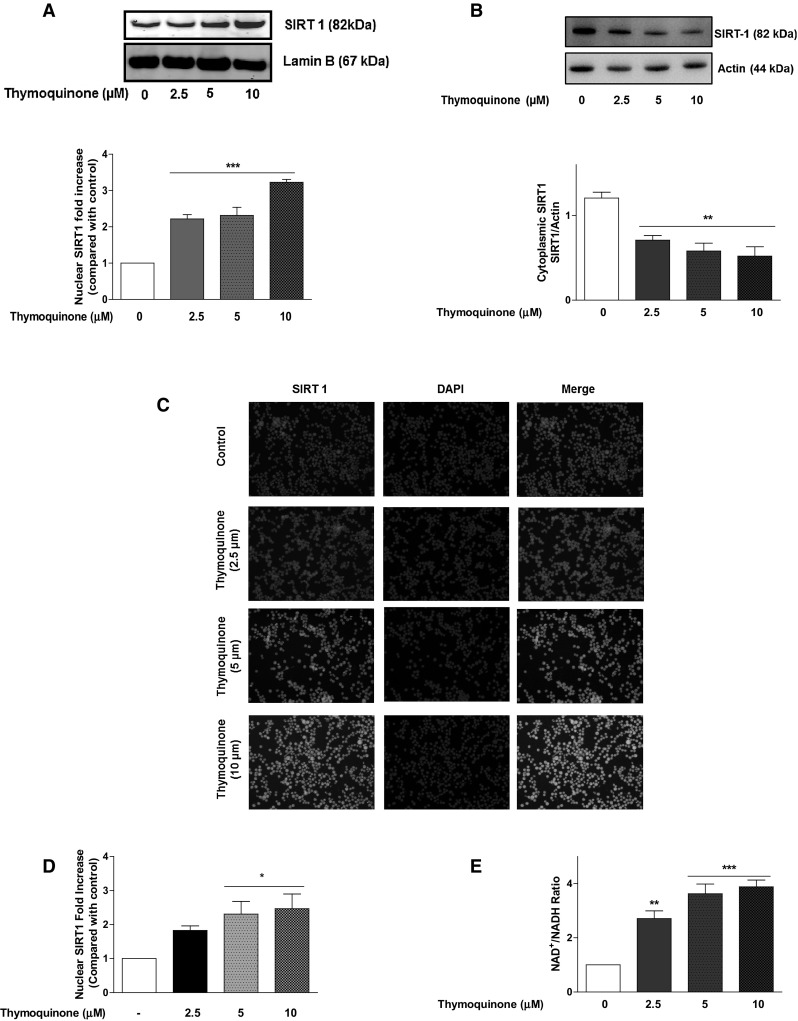
Thymoquinone activates SIRT1 in BV2 microglia. a BV2 cells were treated with vehicle or thymoquinone (2.5–10 µM) for 12 h. Nuclear extracts were analysed using immunoblotting for SIRT-1 and lamin B. Representative blots and densitometric analyses of three independent experiments are shown (Mean ± SEM; ***p < 0.001; one-way ANOVA). b BV2 cells were treated with vehicle or thymoquinone (2.5–10 µM) for 12 h. Cytoplasmic extracts were analysed using immunoblotting for SIRT-1 and actin. Representative blots and densitometric analyses of three independent experiments are shown (Mean ± SEM; **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001; one-way ANOVA with ANOVA post hoc Student Newman–Keuls test). c Immunofluorescence showing nuclear SIRT1 following treatment of BV2 cells with thymoquinone for 12 h. d BV2 cells were treated with vehicle or thymoquinone (2.5–10 µM) for 12 h. Nuclear extracts were analysed using mouse ELISA for SIRT1. (Mean ± SEM; *p < 0.001; one-way ANOVA). e Thymoquinone increases levels of NAD+ in BV2 microglia. (Mean ± SEM; **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001; one-way ANOVA with ANOVA post hoc Student Newman–Keuls test)
