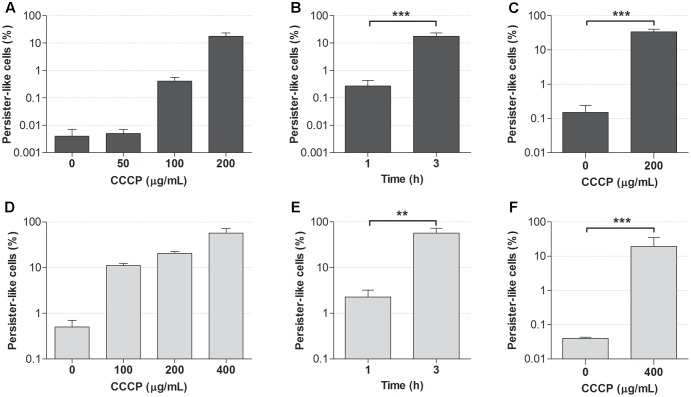
FIGURE 2.
Effect of CCCP on the induction of persistence in stationary-phase cultures of P. aeruginosa ATCC 27853 (A–C) and S. aureus ATCC 33591 (D–F). Ability of different concentrations of CCCP to induce a persister-like status was assessed by evaluating the percentage of cells surviving the treatment with ciprofloxacin (5 μg/mL) (A) or levofloxacin (2.5 μg/mL) (D) following 3-h exposure to CCCP. Optimal exposure time to CCCP was assessed based on cell survival to ciprofloxacin (5 μg/mL) (B) or levofloxacin (2.5 μg/mL) (E) following a pretreatment of 1 or 3 h with CCCP at 200 μg/mL (for P. aeruginosa) or 400 μg/mL (for S. aureus). Susceptibility of P. aeruginosa to meropenem (10 μg/mL) (C) and S. aureus to gentamicin (10 μg/mL) (F) was determined following a pretreatment of 3 h with CCCP. Data are reported as mean ± standard error of the mean of at least three independent experiments. ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001 (one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey-Kramer post hoc test).