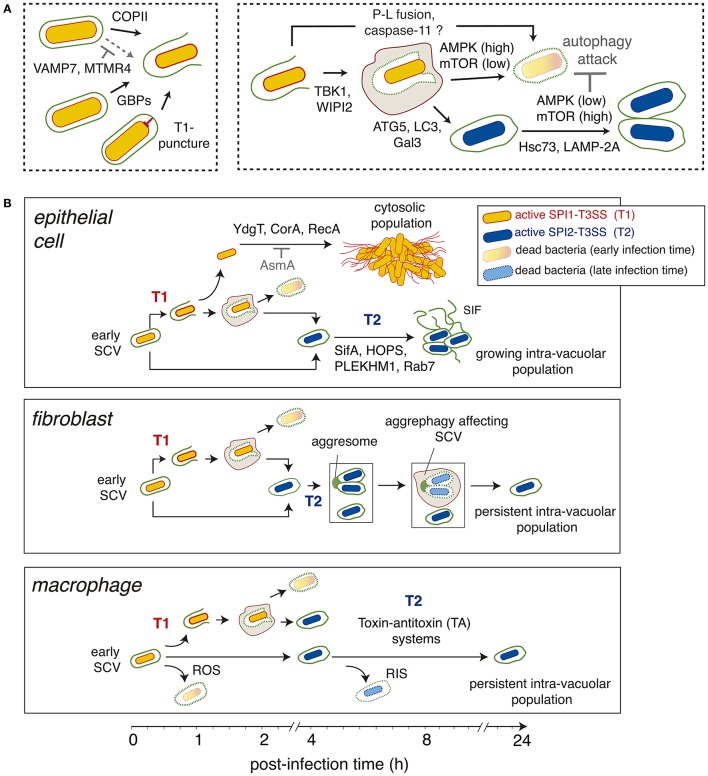
Figure 3.
Different stages and main regulatory factors (host and pathogen origin) modulating the generation of the cytosolic and intra-vacuolar Salmonella populations. (A) Steps influencing the generation of cytosolic and intra-vacuolar populations. The factors involved are indicated. Those cases in which the effect is inhibitory are highlighted in gray; (B) Scheme depicting the main stages characterized in various host cell types (epithelial cell, fibroblasts, macrophages) regarding the generation of distinct bacterial populations as the infection progresses overtime. Factors known to contribute to defined steps are indicated. Abbreviations: AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; ATG5, autophagy protein 5; COPII, coat protein complex-2; Gal3, galectin-3; GBPs, guanylate-binding proteins; HOPS, homotypic fusion and vacuole sorting complex; Hsc73, heat shock cognate protein 73; LAMP-2A, receptor for chaperone-mediated autophagy; LC3, microtubule-associated proteins 1A/1B light chain 3B; MTMR4, myotubularin-4; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; PLEKHM1, Pleckstrin homology domain-containing protein family member 1; P-L fusion, phagosome-lysosome fusion; RNS, reactive nitrogen species; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SCV, Salmonella-containing vacuole; SIF, Salmonella-induced filaments; T1, SPI1-encoded type III secretion system; T2, SPI2-encoded type III secretion system; VAMP7, vesicle membrane-associated protein 7; TBK1, Tank-binding kinase 1; WIPI2, WD repeat domain phosphoinositide-interacting protein 2.