Fig. 3.
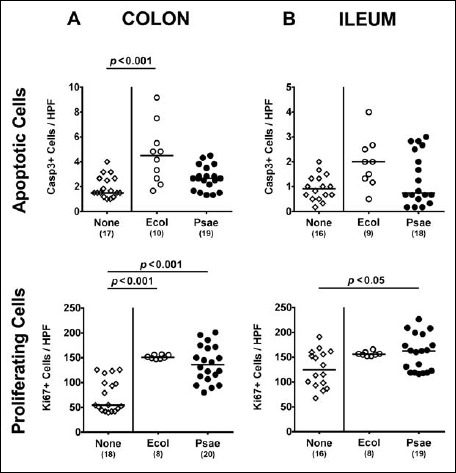
Apoptotic and proliferating intestinal epithelial cells following peroral MDR P. aeruginosa association of secondary abiotic mice. Secondary abiotic mice were perorally associated with a murine commensal E. coli (Ecol, white circles) or a multidrug resistant P. aeruginosa strain (Psae, black circles) on day (d) 0. Four weeks thereafter (i.e., on day 28 postinfection), the average numbers of epithelial apoptotic (positive for caspase 3, Casp3; upper panel) and proliferating cells (positive for Ki67; lower panel) were determined in ex vivo biopsies derived from the (A) colon (left panel) and (B) ileum (right panel) in six high power fields (HPF, 400× magnification) per animal in immunohistochemically stained intestinal paraffin sections. Uninfected mice (none; open diamonds) served as negative controls. Numbers of mice, medians (black bars), and significance levels (p values) determined by the Mann–Whitney U test are indicated. Data shown were pooled from three independent experiments
