Fig. 4.
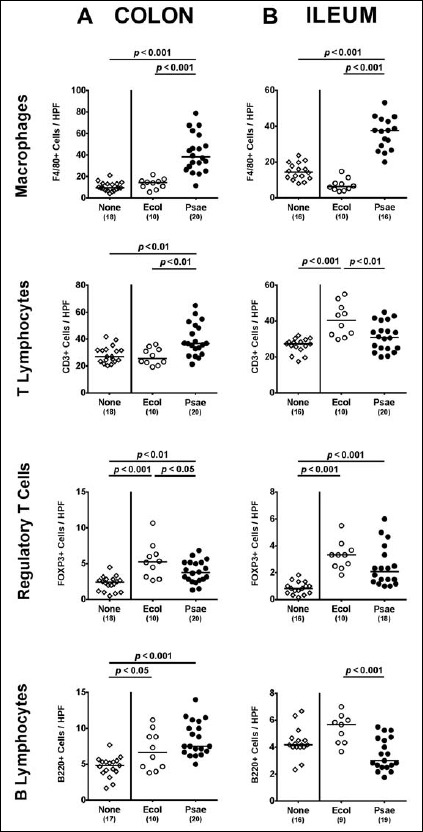
Intestinal immune cell responses following peroral MDR P. aeruginosa association of secondary abiotic mice. Secondary abiotic mice were perorally associated with a murine commensal E. coli (Ecol, white circles) or a multidrug resistant P. aeruginosa strain (Psae, black circles) on day (d) 0. Four weeks thereafter (i.e., on day 28 postinfection), the average numbers of macrophages and monocytes (positive for F4/80), colonic T lymphocytes (positive for CD3), regulatory T cells (positive for FOXP3), and B lymphocytes (positive for B220) were determined in ex vivo biopsies derived from the (A) colon (left panel) and (B) ileum (right panel) in six high power fields (HPF, 400× magnification) per animal in immunohistochemically stained intestinal paraffin sections. Uninfected mice (none; open diamonds) served as negative controls. Numbers of mice, medians (black bars), and significance levels (p values) determined by the Mann–Whitney U test are indicated. Data shown were pooled from three independent experiments
