Fig. 6.
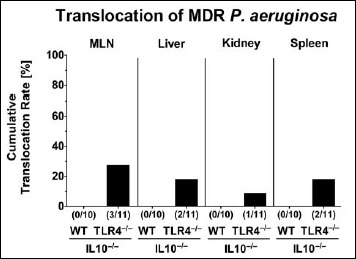
Bacterial translocation to extra-intestinal compartments in multidrug-resistant P. aeruginosa-colonized secondary abiotic IL10–/– mice lacking TLR4. Secondary abiotic IL10-deficient (WT IL10–/–; white bars) and TLR4-deficient IL10–/– mice (TLR4–/– × IL10–/–; black bars) were perorally challenged with a clinical multidrug-resistant P. aeruginosa strain (day 0). Two weeks thereafter, viable bacteria were detected in ex vivo biopsies derived from mesenteric lymph nodes (MLN), liver, kidney, and spleen by culture and the cumulative translocation rates out of three independent experiments indicated in %. Numbers of animals harboring the P. aeruginosa strain out of the total number of analyzed animals are given in parentheses
