Figure 2.
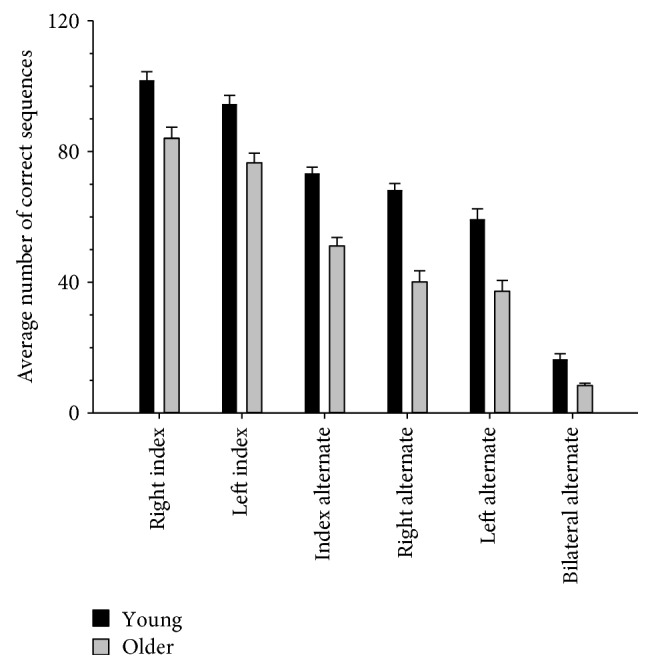
Motor performance on the six different tapping tasks in young (n = 18) and older (n = 20) adults. The number of correct motor sequences completed was significantly reduced in older compared with younger adults. Overall performance, averaged across the two age groups, declined with tasks involving greater complexity. Error bars denote SEM.
