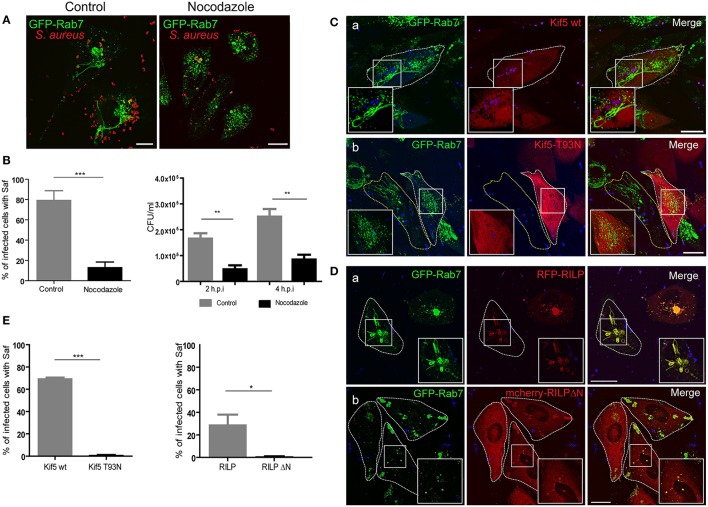
Figure 2.
Microtubules, Kif5 and RILP are necessary for Saf elongation. (A) CHO GFP-Rab7 stably transfected cells were infected for 1 h with S. aureus wt. In the left panel cells were incubated in control media and in the right panel after 30 min post-infection 2 μM nocodazole was added and maintained for the rest of the infection period. (B) The graph on the left shows quantification of the percentage of infected cells with Saf formation in control conditions (gray bar) or treated with nocodazole (black bar). The graph on the right represents the quantification of the number of CFU/ml of CHO cells infected for 2 or 4 h S. aureus wt. Grey bars represent control conditions and black bars indicate cells treated with 2 μM nocodazole. (C) CHO cells stably overexpressing GFP-Rab7 were co-transfected with RFP vector and pcDNA-Kif5 wt (Panel a) or with pcDNA-Kif5T93N (panel b), and then subsequently infected with S. aureus wt for 1 h. (D) CHO GFP-Rab7 stably overexpressing cells were transfected with RFP-RILP wt (Panel a) or with mCherry-RILPΔN (Panel b) and then infected with S. aureus wt for 1 h. Bacteria were labeled with TOPRO. All conditions (A,C,D) were observed as living cells using confocal microscopy. Images are representative of two independent experiments. (E) Graphs show the percentage of cells with Rab7 and Kif5 double positive Safs and the percentage of cells with Safs marked with Rab7 an RILP. In all cases data show mean ± SEM of two independent experiments (n = 100 cells/condition). *P ≤ 0.01, **P≤0.001 ***P ≤ 0.0001 from two-tailed Student t-test. Scale bar: 20 μm.