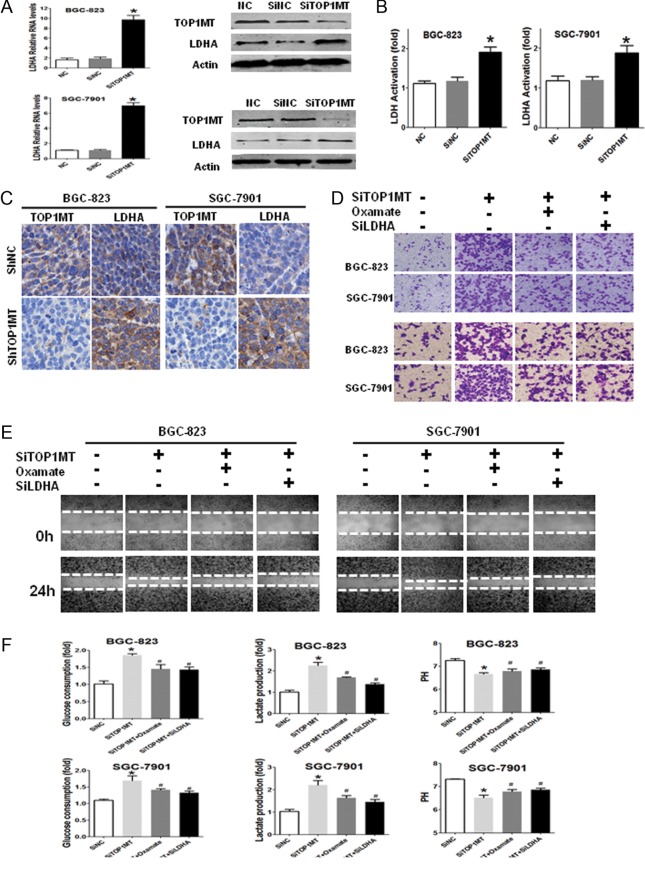
Figure 4.
LDHA was required for the upregulation of migration, invasion and glycolysis in GC cells induced by TOP1MT silencing. (A) RT-PCR and Western blot analysis for the detection of LDHA expression in BGC-823 and SGC-7901 cells. (B) LDHA activation was examined for BGC-823 and SGC-7901 cells using LDHA activity assays. (C) Representative images of immunohistochemical staining of LDHA expression for BGC-823 and SGC-7901 cells in subcutaneous xenografts. LDHA expression significantly increased in BGC-823 and SGC-7901 cells with TOP1MT knockdown. (D, E and F) BGC-823 and SGC-7901 cells transfected with SiTOP1MT and/or cultured with LDHA inhibitor (oxamate sodium or siLDHA) were subjected to transwell migration assays (D, upper), Boyden chamber invasion transwell assays (D, lower) and wound closure assays (E) to analyze the invasion and migration of GC cells. The results demonstrated LDH inhibition counteracted the migration and invasion induced by TOP1MT knockdown. (F) The results showed that LDHA inhibition reversed the enhancement of glucose consumption (F, left), lactate produced (F, middle) in BGC-823 and SGC-7901 cells induced by TOP1MT silencing, leading to PH values increase (F, right). *P < 0.05 in comparisons of the SiTOP1MT-transfected group with the control group. # P < 0.05 in comparisons of the SiTOP1MT with oxamate/SiLDHA group with the SiTOP1MT group. A full colour version of this figure is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1530/ERC-17-0058.

 This work is licensed under a
This work is licensed under a