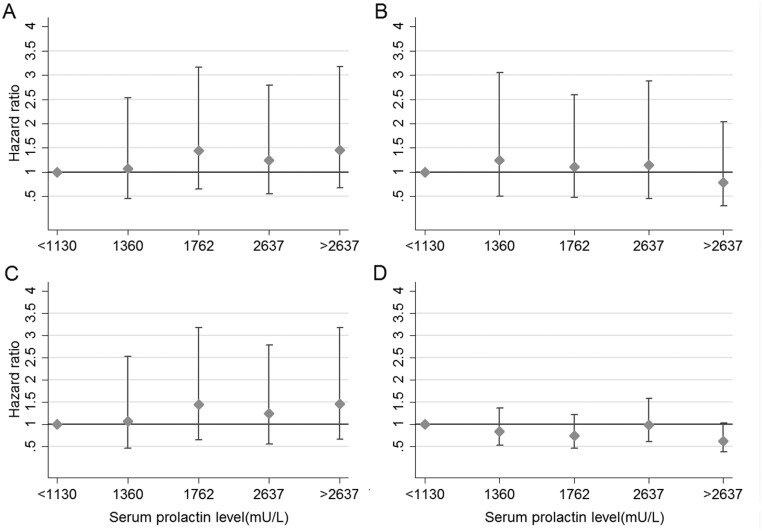
Figure 1.
Estimated HRs (± 95% CI) for several clinical outcomes in patients with hyperprolactinaemia according to serum prolactin levels. Footnote: Quintiles of maximum serum prolactin levels (<1130, 1131–1360, 1361–1762, 1763–2637, >2637 U/L). Hazard ratios calculated using Cox proportional hazards’ models. (A) Diabetes mellitus model adjusted for age and gender. Wald linear test of parameter estimates Chi2 (3) = 3.59, P = 0.30. (B) Non-fatal cardiovascular disease model adjusted for age, gender, history of diabetes mellitus and renal impairment; Wald linear test Chi2 (3) = 0.93, P = 0.81. (C) Bone fractures model adjusted for history of bisphosphonates use, prednisolone use and renal impairment; Wald linear test Chi2 (3) = 0.73, P = 0.86. (D) Mortality model adjusted for age, gender, history of non-fatal cardiovascular disease, renal impairment and a Scottish index of multiple deprivation; Wald linear test Chi2 (3) = 3.26, P = 0.35.

 This work is licensed under a
This work is licensed under a