Figure 1.
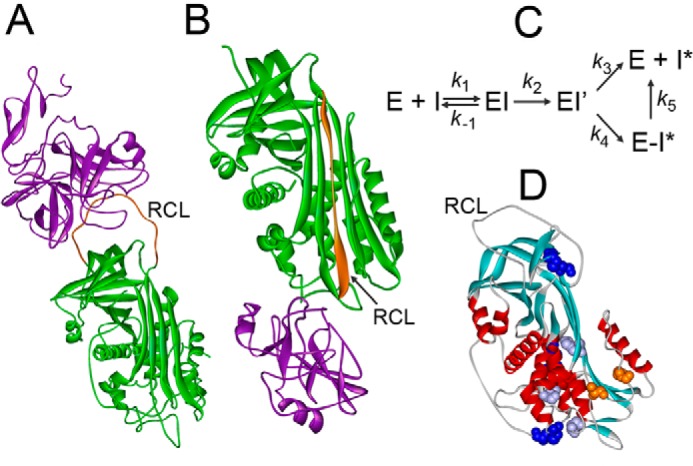
Mechanism of proteinase inactivation by serpins. A, Michaelis complex of S195A FXa and AT (Protein Data Bank code 2GD4). B, covalent complex of α1PI with trypsin (Protein Data Bank code 1EZX). Proteinases are shown in purple, serpins are shown in green, RCL are shown in orange. C, mechanism of enzyme (E) and serpin (I) forming a Michaelis complex (EI), acyl-enzyme (EI′), and partitioning between the substrate (k3) and inhibitory pathway (k4). Unstable E-I* complexes dissociate into free E and cleaved I* (k5). D, native AT with positions of Ser365 and Ile207 (orange); L340F, S349P, and H369Y (purple), and three disulfide bridges (blue) (Protein Data Bank code 1E05).
