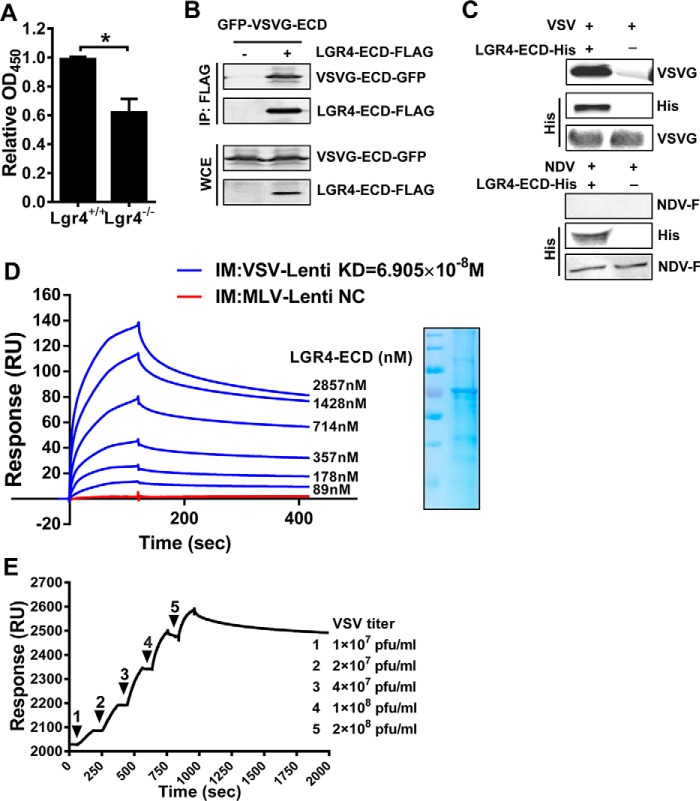
Figure 5.
VSV binds host cells through the extracellular domain of Lgr4. A, the binding of VSV on Lgr4+/+ and Lgr4−/− MEF cells was analyzed by cell-based ELISA. B, HEK293T cells were transfected with plasmids encoding LGR4-ECD-FLAG and VSVG-ECD-GFP for 36 h before lysis. Then the complex was immunoprecipitated by anti-FLAG-agarose followed by immunoblot analysis of VSVG-ECD-GFP and LGR4-ECD-FLAG. C, immunoblotting of VSV-G and LGR4-ECD-His after LGR4-ECD-His and associated proteins were pulled down with nickel beads. Reblotting of the membrane with anti-VSV-G mAb was performed as an input control. NDV is a negative control. D, dose-response of LGR4-ECD binding to immobilized VSVG-LV or MLV-LV by surface plasmon resonance in PBS. VSVG-LV or MLV-LV were immobilized on a CM5 sensor chip, and LGR4-ECD was passed at the indicated concentrations. MLV-LV as a negative control (NC) was shown with a concentration of 714 nm LGR4-ECD. SDS-PAGE of LGR4-ECD is shown on the right. IM, immobilize: VSVG-LV (blue), MLV-LV (red). E, dose-response of VSV binding to immobilized LGR4-ECD by surface plasmon resonance in PBS. LGR4-ECD (20 μg/ml) was immobilized on a sensor chip NTA, and VSV was passed at the indicated concentrations. The kinetic constants of binding were obtained using a 1:1 Langmuir binding model via BIAevaluation software. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments. Asterisks indicate statistical significance: *, p < 0.05.