Figure 6.
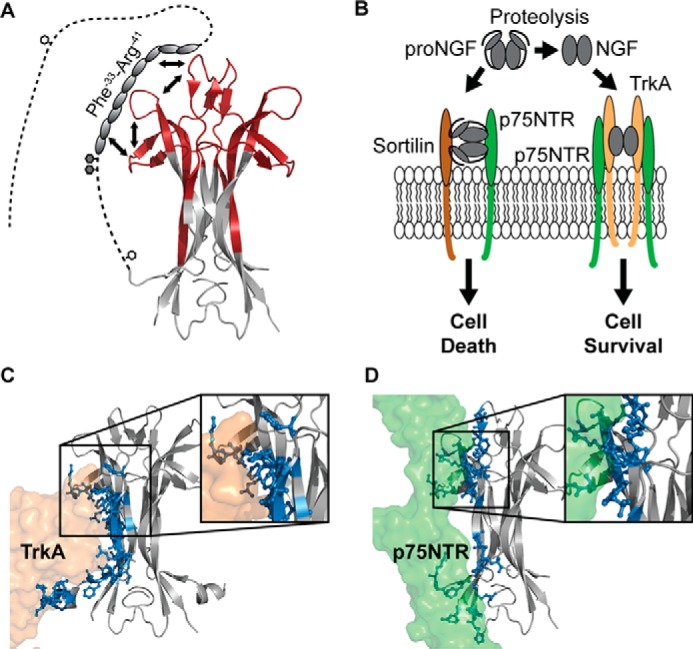
A refined structural model of proNGF. A, schematic representation of the findings presented in the current study. We propose that the part of the pro-part where local higher-order structure was identified interacts with parts of loops I, II, and IV via a combined intra- and intermolecular mechanism. The white hexagons mark N-linked glycosylation sites, and the gray hexagons mark O-linked glycosylation sites. To decrease the complexity, the pro-part was included on only one of the NGF monomers (PDB ID: 1SG1). B, biological effect of proNGF and NGF on neurons. NGF induces the growth of neurons by binding to the TrkA and the p75NTR receptors, whereas proNGF mediates apoptosis of neurons by binding to a receptor complex of sortilin and p75NTR. Figure adapted from (8). C and D, crystal structures of NGF (gray) in complex with TrkA (orange) and p75NTR (green) (PDB ID: 2IFG and 1SG1). Residues in NGF that form hydrogen bonds with the receptors are highlighted as sticks and colored blue. Inserts, zoom image of the binding surface implicating loops I, II, and IV of NGF. To simplify this figure, the second receptor molecule of TrkA and p75NTR was omitted.
