Figure 1.
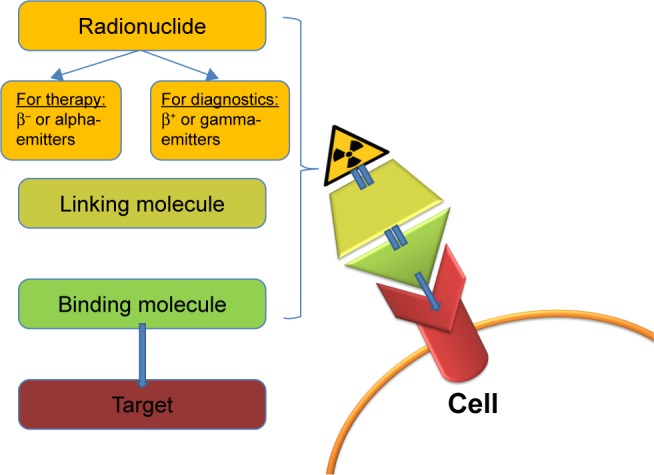
The theranostic principle in nuclear medicine involves combining diagnostic imaging and therapy with the same molecule, which is radiolabeled differently, or administered in other dosages. In case of radioiodine therapy (RAI), the radioisotope (131I or 123I) can be directly mediated by the sodium-iodide symporter in the thyroid cells. In other cases, it can be more complex. The image shows a simplified model of a radiopharmaceutical, which consists of a binding molecule that binds the target, and a linking molecule, which binds the radioisotope. Examples of such theranostic molecules are DOTA-TOC, DOTA-TATE, and PSMA-617.
