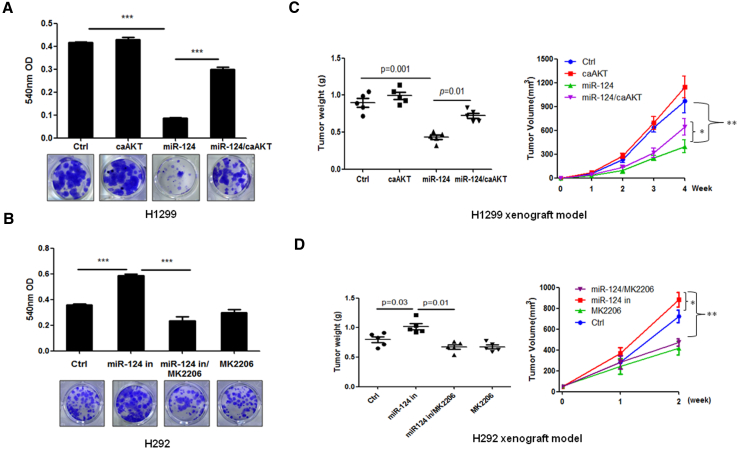
Figure 3.
miR-124 Inhibits NSCLC Growth through the Suppression of the Akt Pathway
(A) The overexpression of miR-124 inhibited colony formation, whereas the constitutive activation of Akt blocked miR-124-induced inhibition of colony formation in H1299 cells. H1299 cells were transfected with indicated plasmid for 24 hr and then subjected to colony-formation assay. (B) The inhibition of miR-124 stimulated colony formation, whereas the inactivation of Akt by MK2206 blocked miR-124 inhibition-induced colony formation in H292 cells. H292 cells were transfected with indicated plasmid for 24 hr then subjected to colony-formation assay. Cells were treated with or without MK2206 every 3 days. (C) Constitutive activation of Akt attenuated miR-124-induced tumor growth inhibition effect in H1299 xenograft models. Stably expressing miR-124 H1299 cells were transfected with plasmid that expression of constitutively active Akt then injected subcutaneously into nude mice (2 × 106 cells per mouse). Tumor volume was measured every week, and after 1 month of cell injection, mice were sacrificed and the tumors were weighed. (D) Inactivation of Akt by MK2206 suppressed miR-124 inhibition-stimulated tumor growth in H292 xenograft models. Control or stably expressing miR-124 antisense H292 cells were injected subcutaneously into nude mice (2 × 106 cells per mouse). When the tumor size was approximately 50 mm3, the mice were administered 6 mg/kg MK2206 or vehicle buffer twice daily by oral gavage. Tumor volume was measured every week, and after 2 weeks of drug treatment, the mice were sacrificed, and the tumor weights were measured. Ctrl, vector control; miR-124 in, miR-124 inhibitor; caAKT, constitutive activation of Akt; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.