Fig. 6.
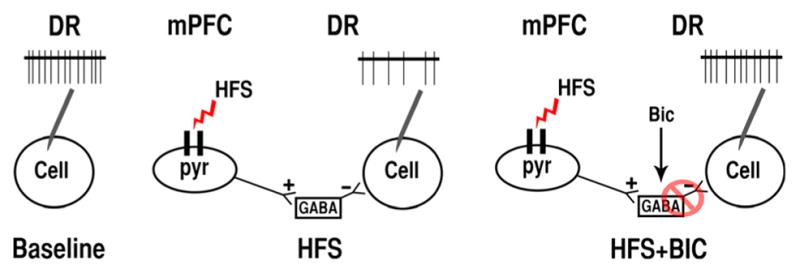
Illustration of the effects of bicuculline (Bic) on neurons in the dorsal raphe (DR) that were inhibited by high-frequency stimulation (HFS) of the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC). HFS activates the excitatory glutamatergic mPFC projections that preferentially innervate GABA neurons in the DR, thus increasing inhibitory GABAergic tone and decreasing cellular firing of recorded neurons (middle illustration). Local administration of Bic blocks GABAA receptors on the recorded cells, disinhibiting the firing rate of the recorded cell, and thereby cancelling the inhibitory effect of HFS.
