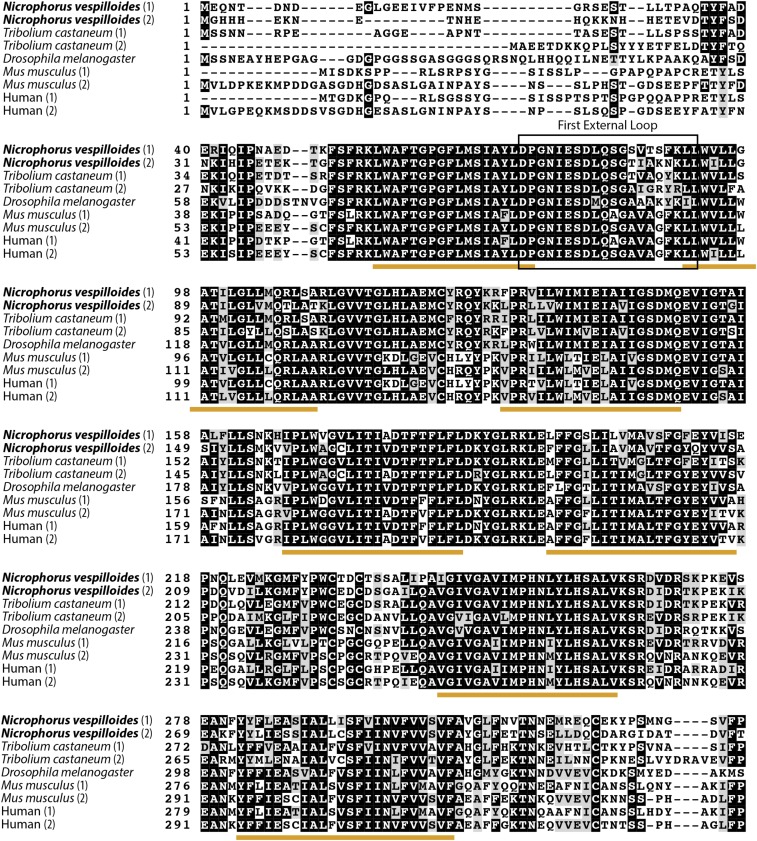
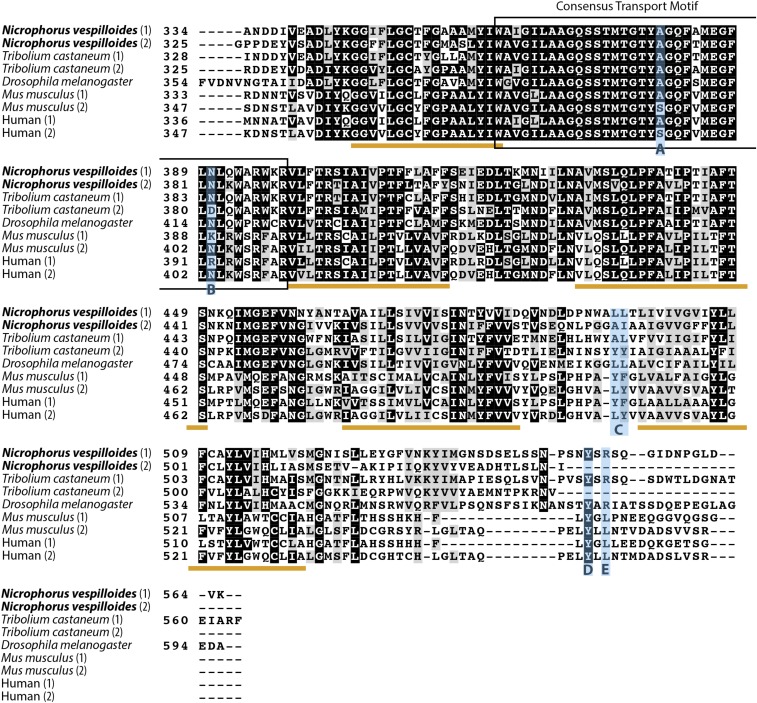
Figure 1.
Amino acid alignment of N. vespilloides Mvl1 and Mvl2, T. castaneum Mvl1 and Mvl2, D. melanogaster Mvl, and the homologous M. musculus and human Nramp1 and Nramp2. Shaded regions represent a >50% similarity among sequences. Underlined sequences indicate putative transmembrane domains, while other regions of interest are indicated by labeled boxes. Specific amino acids of interest are highlighted and labeled with a letter. A, B, and C represent amino acids that indicate symporter or antiporter activity, with the following patterns; A:S indicates symporter, A indicates antiporter, B:N or D indicates symporter, K or R indicates antiporter, C: LY indicates symporter, and YF indicates antiporter. D and E are conserved amino acid positions that are part of the intracellular localization motif, which determines the intracellular localization of the protein in humans (Tabuchi et al. 2002).