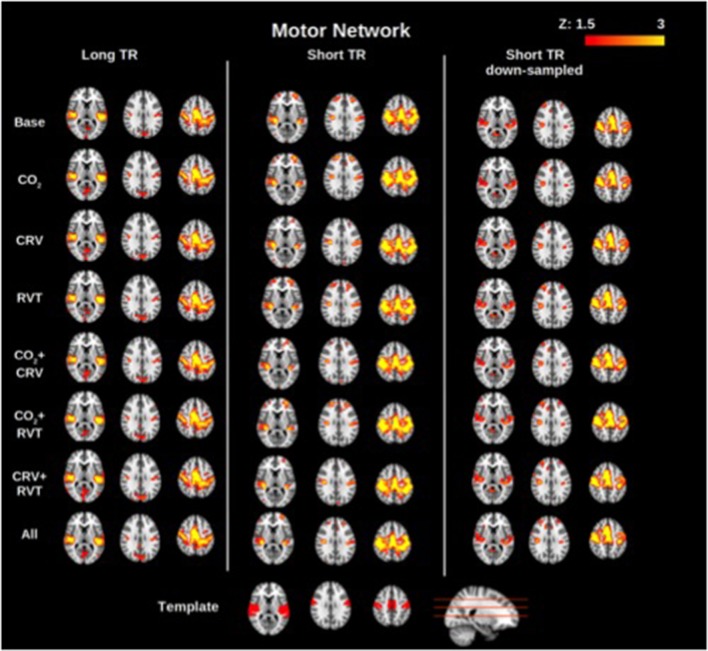
Figure 2.
Group-averaged motor network (MN) connectivity maps generated with different physiological correction strategies, using long-TR, short-TR, and down-sampled short-TR data. A motor network template from the atlas generated by Yeo et al. (2011) is shown at the bottom for reference. CRV correction alters connectivity maps more than correction for PETCO2 (labeled as CO2) and RVT by reducing the extent of connected clusters outside the motor cortex. Sampling-rate does not seem to have a considerable effect on the connectivity maps.