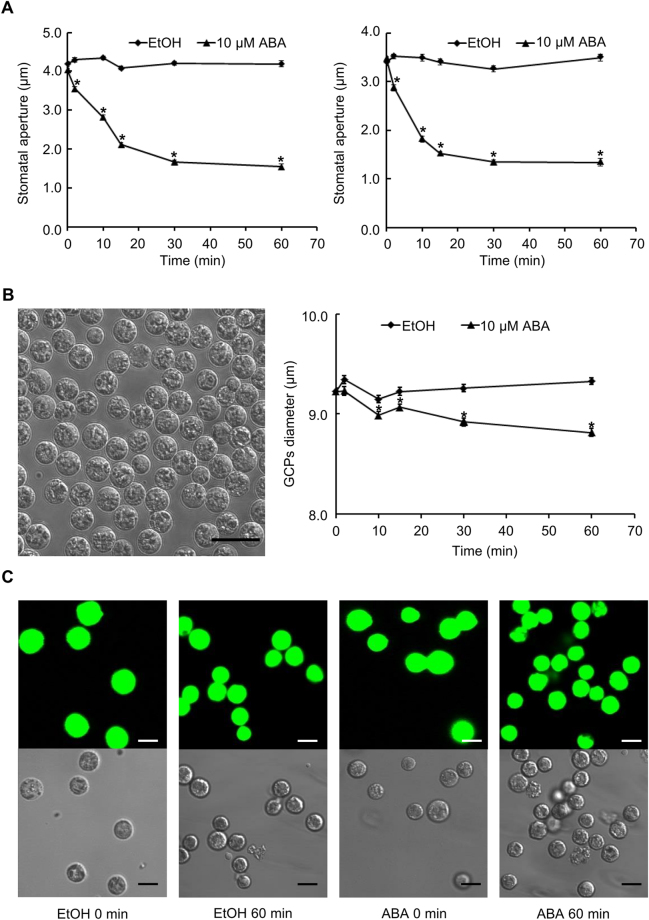
Figure 1.
Responses to ABA in B. napus leaves, epidermal peels, and guard cell protoplasts. (A) ABA (10 µM) induces stomatal closure in both leaf pieces (left panel) and epidermal peels (right panel) of B. napus line DH12075. Data are means ± standard errors of 3 independent replicates with 100 ± 5 stomata measured for each sample. (B) ABA-induced shrinkage of B. napus GCPs. Representative image (left); scale bar indicates 25 µm. Data (right) are means ± standard errors of 4 independent replicates with 100 ± 5 GCPs measured for each sample. (C) B. napus GCPs are viable following ABA or ethanol (solvent control) treatment. Samples before treatment (0 min) and after treatment (ethanol (EtOH) 60 min and ABA 60 min) were FDA stained to assess cell viability. Scale bars indicate 10 µm. Asterisks in A and B indicate that ABA treatment differed significantly from the EtOH solvent control (Student’s t test; p < 0.05).