Figure 3.
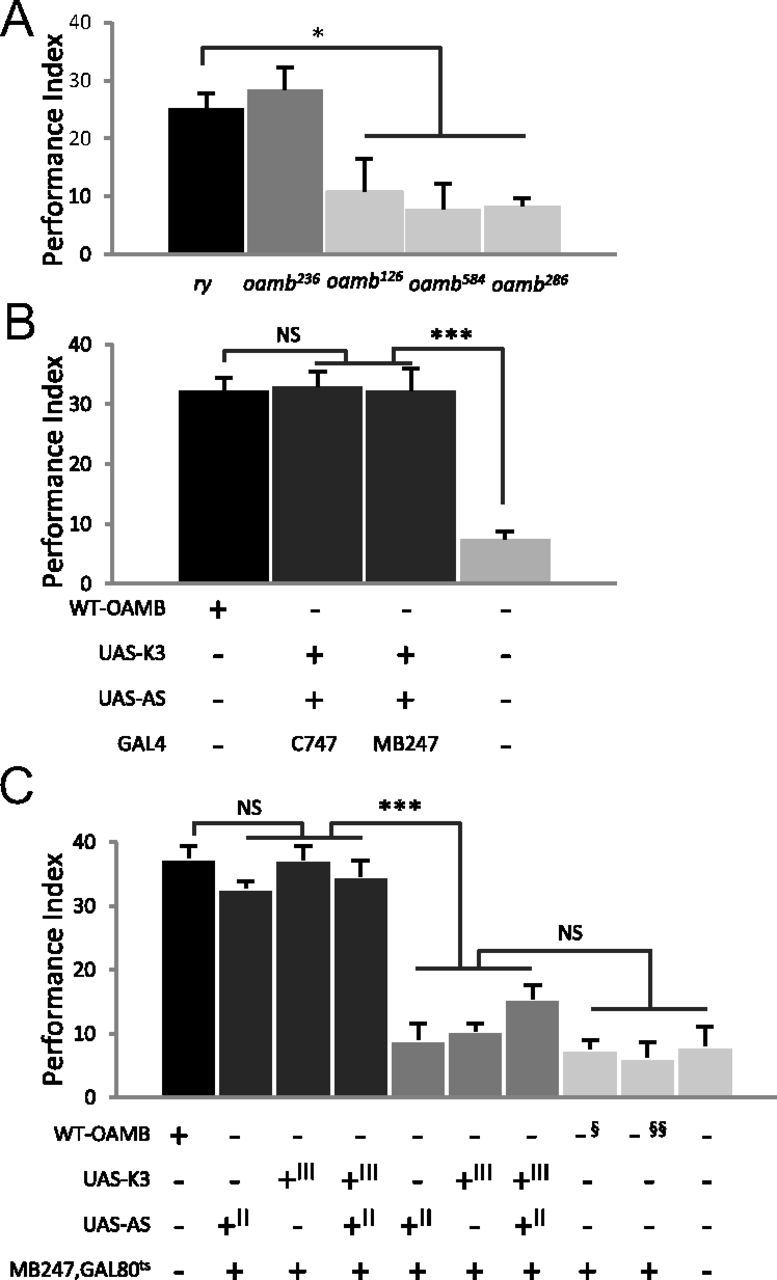
The OAMB's functional site for appetitive learning is the mushroom body αβ and γ neurons. A, Behavioral analysis of hypomorphic oamb alleles. oamb236 with normal mushroom body OAMB expression displayed performance comparable to that of the ry control; however, oamb126 with significantly reduced mushroom body OAMB showed severe deficit in acquisition of appetitive memory like oamb286- and oamb584-null mutants (n = 6–18). B, Transgenic OAMB expression induced by the mushroom body driver C747-GAL4 or MB247-GAL4 during development and adulthood fully rescued the oamb's learning phenotype (n = 6–17). C, Normal appetitive learning in oamb mutants was reinstated by temporarily restored OAMB-K3 or OAMB-AS or both in the adult mushroom body αβ and γ neurons. The oamb mutants carrying MB247-GAL4 and tubP-GAL80ts along with UAS-OAMB-K3 or UAS-OAMB-AS or both, upon mild heat treatment before training (dark gray columns), showed learning performance comparable to that of Canton-S (n = 6 for each genotype). The same genotypes without heat treatment (mid-gray columns) or the oamb286 (§) and oamb286/oamb96 (§§) carrying only MB247-GAL4 and tub-GAL80ts subjected to the same temperature shift (light gray columns), however, showed poor learning similar to oamb286. II and III in the genotype table denote the chromosomes containing the transgene. NS, Not significant; *p < 0.05; ***p < 0.001, Tukey–Kramer.
