Fig. 2.
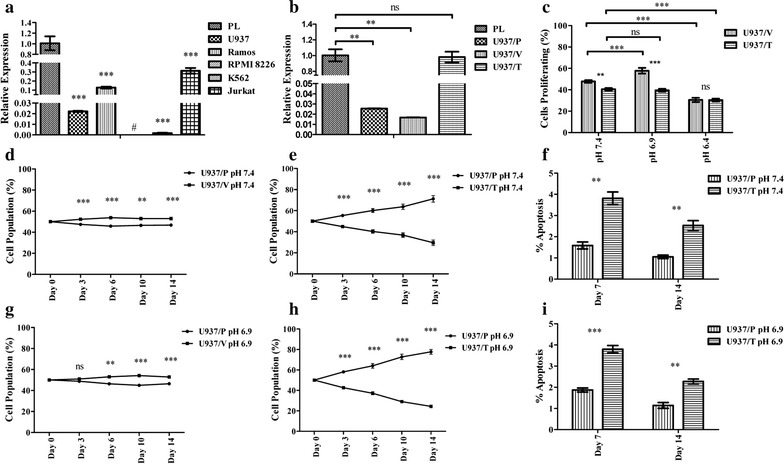
Restoration of TDAG8 gene expression in U937 cells provides a growth disadvantage at physiological pH 7.4 and mildly acidic pH 6.9. a Quantitative RT-PCR demonstrates a reduction of TDAG8 gene expression in U937, ramos, RPMI 8226, K562, and Jurkat cells in comparison to peripheral leukocytes pooled from 426 healthy donors. b Quantitative RT-PCR demonstrates restoration of TDAG8 gene expression in U937 acute myeloid leukemia cells following transduction and cell sorting. c Mild acidosis (pH 6.9) increases U937/Vector cell proliferation while severe acidosis (pH 6.4) inhibits cell proliferation. Restoring TDAG8 gene expression in U937 cells inhibits cell proliferation in comparison to U937/Vector cells. d The expression of the empty MSCV-IRES-GFP construct in U937 cells does not substantially affect the U937/Vector cell population percentage in comparison to U937/Parental cells at pH 7.4 from day 0 to day 14. e The restoration of TDAG8 gene expression in U937 cells reduces cell growth in comparison to U937/Parental cells at physiological pH 7.4. f Restoring TDAG8 gene expression in U937 cells increases apoptosis throughout the cell competition assay at pH 7.4. g The expression of the empty MSCV-IRES-GFP construct in U937 cells does not substantially affect the U937/Vector cell population percentage in comparison to U937/Parental cells at pH 6.9 from day 0 to day 14. h The difference between the U937/TDAG8 cell population and the U937/Parental cell population throughout the competition assay at acidic pH 6.9 is greater in comparison to pH 7.4 treatment. i Restoring TDAG8 gene expression in U937 cells increases apoptosis throughout the cell competition assay at pH 6.9. Pooled RNA from 426 normal peripheral leukocytes was purchased from Clontech Laboratories, Inc. to be used as a control for a healthy immune cell comparison. ns: P > 0.05, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001
