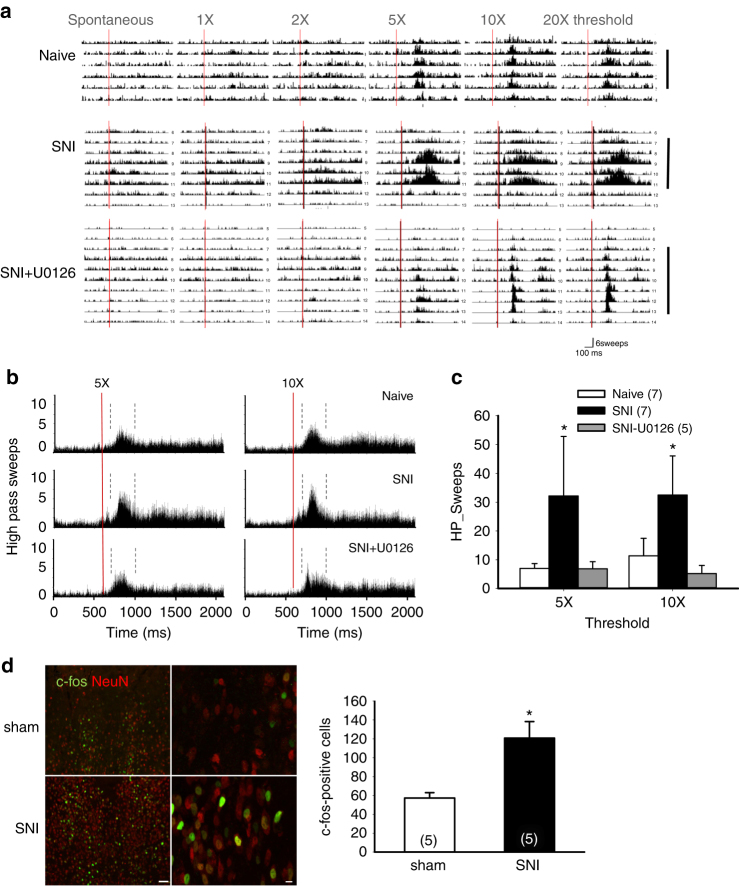
Fig. 4.
Neuronal activities of PVA increase in SNI-induced neuropathic pain model. a Representative sweeps of spike firing of PVA neurons in naïve mouse, SNI, and SNI with intra-PVA U0126 infusion groups in response to different strength of stimulations. The red line indicates the electrical stimulation on the left sciatic nerve. There is no current input in the spontaneous recording. The black line on the right indicates those channels in PVA region. b The average of evoked sweep spike summation from 5 to 7 mice in each experimental groups responding to the stimulation current 5 and 10 times to the threshold, respectively. PVA neuron sweep spike are segregated into FC, and LC defined by the spike pattern (responding to the stimulation faster or slower than 400 ms). The first and second dash lines indicate 100 and 400 ms after electrical stimulation, respectively. c Sweep spikes of 0–100 ms FCs in different groups. The summation of sweep spikes responding to different strength of electrical stimulus of each component was analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed a post hoc testing method. *p < 0.05 compared to naïve group and to SNI-U0126 group. d Immunofluorescent imaging of c-fos (green) and NeuN (red) in PVA from sham and SNI animals. Scale bar = 50 μm (left panel) and 10 μm (right panel), respectively. *p < 0.05 compared to sham group. Error bars indicate SEM. Statistical significance was determined by Student’s t-test (d)