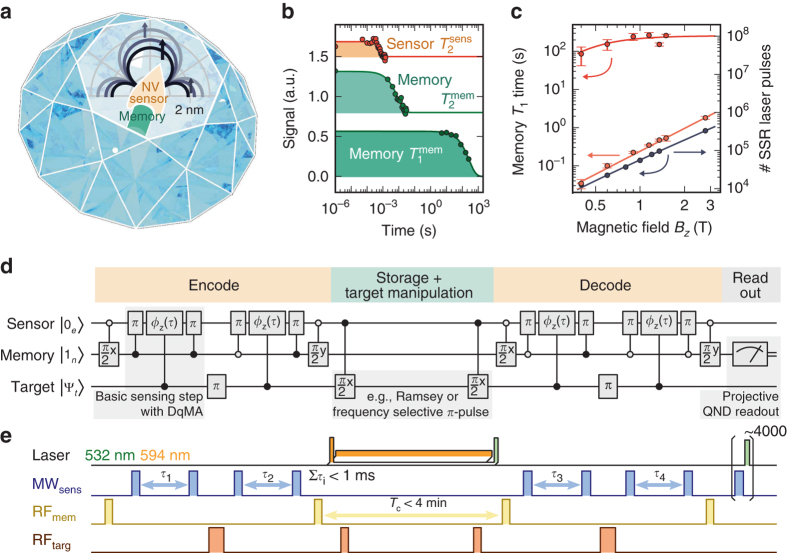
Fig. 1.
The combined sensor–memory spin system. a Schematic representation of the sensor–memory pair comprising the electron and 14N nuclear spin of an NV center in diamond. The inset sketches potential locations of 13C target spins detected in this work. b Longitudinal and transverse relaxation times (T 1, T 2) of sensor and memory spin (sens, mem). c -scaling with magnetic field strength for three cases: NV center in the negative (red line), the neutral charge state (orange line), and during continuous memory readout (gray line). The shown errors correspond to the standard error of the exponential fit to the decay of the spin state. d, e Wire diagram and pulse sequence representation of an exemplary Ramsey measurement of target spins, sub-divided into four tasks: encoding; storage, and manipulation; decoding and readout. During encoding and decoding, the sensor phase ϕ (dependent on target spin state and duration τ i) is transferred onto a memory superposition state. This process is efficiently performed by entangling and disentangling sensor and memory with CmROTs-gates granting the sensor direct quantum memory access (DqMA). Proper conditions of the CmROTs-gates (i.e., open (closed) circle → sensor π-flip for memory state “0” (“1”)) enable sensitivity to target spins and protection against quasi-static magnetic field noise (see “Methods”). Memory spin π/2 pulses (phases given by subscripts x and y) switch between quantum (i.e., ) and classical (i.e., = sin ϕ) information storage. Between subsequent basic sensing steps, target spins are flipped, during central storage, this is achieved with high spectral resolution via Ramsey interferometry (i.e., two RF π/2 pulses). Appropriate Laser illumination enables continuous sensor repolarization into , or ionization into the neutral NV0 for decoupling of sensor and target spins during central storage. During decoding, the current target spin state is correlated with its encoded initial state stored as expectation value on the memory. Finally, the memory state is readout in a single shot32