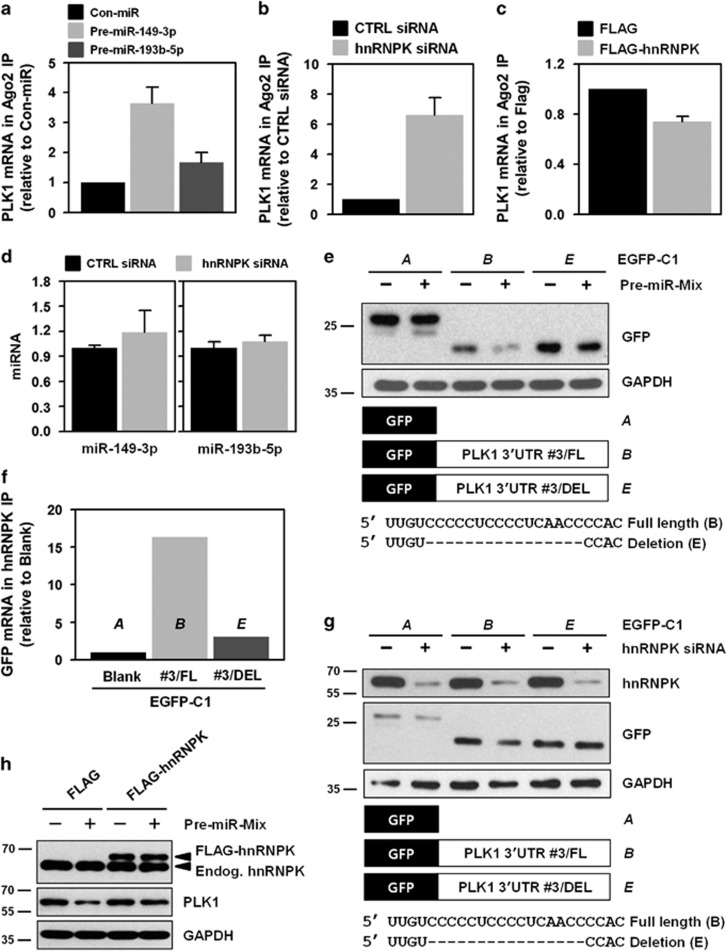
Figure 5.
Competitive regulation of PLK1 by hnRNPK and miR-149-3p/193b-5p. (a) Cytoplasmic lysates were obtained from miR-149-3p- or miR-193b-5p-overexpressing cells and immunoprecipitated (IP) with Ago2-specific antibody. Enrichment of PLK1 mRNA in Ago2 IP was assessed by RT–qPCR. (b,c) To investigate the effect of hnRNPK on the interaction between PLK1 mRNA and an miRNA-loaded RISC complex, enrichment of PLK1 mRNA in Ago2 IP was examined using cytoplasmic lysates obtained from hnRNPK-silenced (b) or -overexpressing (c) HeLa cells. The level of PLK1 mRNA in Ago2 IP was assessed by RT–qPCR. (d) To test whether hnRNPK affects expression of miR-149-3p and miR-193b-5p, cells were transfected with control or hnRNPK siRNA. After 48 h post-transfection, miRNA expression levels were determined by RT–qPCR. (e) To examine the effect of miRNA mimics on GFP expression, GFP reporters were generated in which GFP was linked to fragment #3 harboring or lacking the binding sequence for hnRNPK and the miRNAs (GFP vector B and E in the schematic). GFP expression was assessed by western blot. (f) The interaction between hnRNPK and GFP chimeric mRNAs was examined. Cells were transfected with the previously described GFP vectors and cytoplasmic lysates were prepared. GFP mRNA enrichment was measured by RNP IP using hnRNPK antibody followed by RT–qPCR. (g) To test whether hnRNPK affects GFP expression in the absence of an miRNA-binding sequence, GFP reporters described in e were used. The expression levels of hnRNPK and GFP were assessed by western blot. (h) To determine whether hnRNPK restored PLK1 expression, cells were transfected with miRNA mimics (pre-miR-149-3p and miR-193b-5p) and an hnRNPK vector (FLAG-hnRNPK). Expression of hnRNPK and PLK1 was assessed by western blot. All experiments were performed more than three times and data represent mean±S.D.