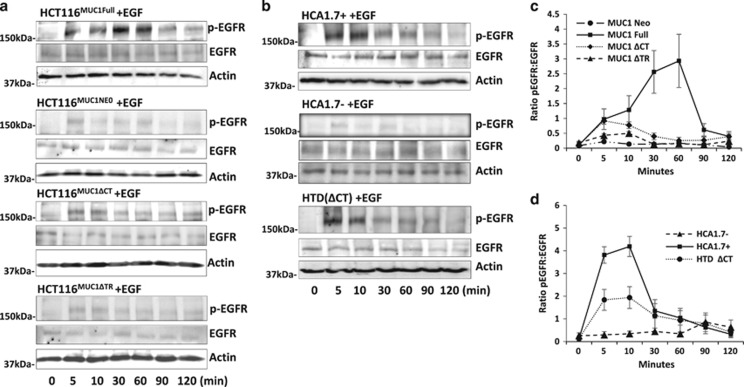
Figure 2.
Both MUC1 extra- and intra-cellular domains influence EGF-induced EGFR activation. MUC1 transfectants of human colon (a) and breast (b) epithelial cells were treated with 20 ng/ml EGF for various times before EGFR phosphorylation were analysed by immunoblotting. The blots were also probed with anti-actin antibody for protein loading. Densitometry scanning of the bands from three independent experiments is shown in (c,d) and is expressed as ratio p-EGFR/EGF (mean±S.E.M.). The cells transfected with full-length MUC1 showed rapid EGFR phosphorylation while the MUC1-negative cells showed little response. Depletion of the MUC1 extracellular domain largely reduced, while depletion of the MUC1 intracellular domain moderately reduced, EGFR phosphorylation in comparison to the cells express full-length MUC1. Representative blots are shown in a and b