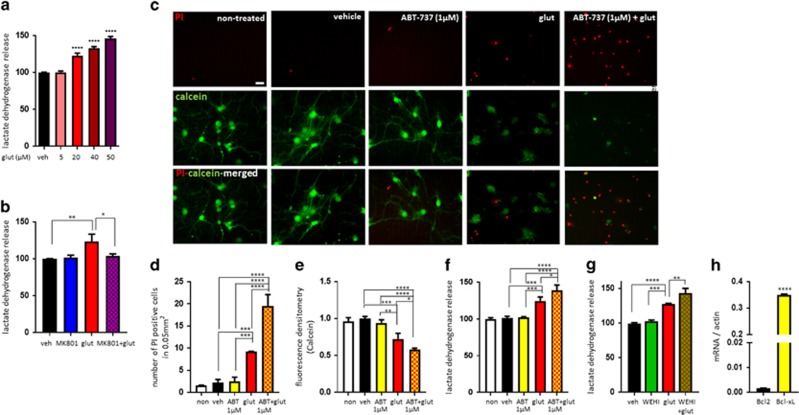
Figure 1.
ABT-737/WEHI-539 aggravates glutamate-induced neuronal toxicity. Primary hippocampal neurons were treated with glutamate (5-50 μM) for 24 h. (a) LDH release (n=3 plates from one culture). Neurons were treated with MK801 (0.1 μM), glutamate (20 μM) or a combination of both for 24 h. (b) LDH release (n=3 independent cultures). (c-f) Neurons were treated with ABT-737 (1 μM), glutamate (20 μM) or a combination of both for 24 h. (c) PI and calcein-stained neurons. Green: calcein; red: PI. Scale bar=20 μm. (d) The number of PI-positive cells (n=3 independent cultures). (e) Calcein retention (n=3 independent cultures). (f) LDH release (n=3 independent cultures). (g) Primary hippocampal neurons were treated with WEHI-539 (5 μM), glutamate (20 μM) or a combination of both for 24 h. Bar graph shows LDH release level (n=3 independent cultures). (h) Quantification of Bcl2 or Bcl-xL mRNA level (n=3 independent cultures). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 and ****P<0.0001, one-way ANOVA