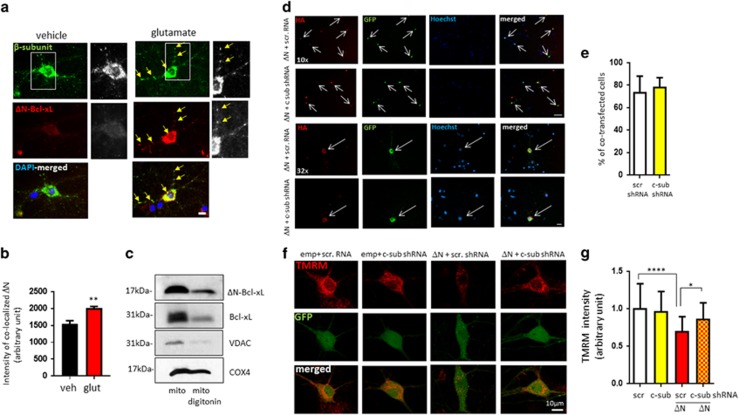
Figure 7.
Depletion of ATP synthase c-subunit protects from ΔN-BcL-xL-induced mitochondrial membrane potential loss. (a) Immunocytochemistry of cultured hippocampal neurons showing co-localization of the β-subunit of ATP synthase with ΔN-Bcl-xL. Green: β-subunit of ATP synthase; red: ΔN-Bcl-xL. (b) fluorescence intensity of ΔN-Bcl-xL at the β-subunit spots (n=3 independent cultures). This shows that ΔN-Bcl-xL amount is enhanced at the mitochondrial inner membrane after glutamate treatment. (c) Immunoblot of ΔN-Bcl-xL, Bcl-xL, VDAC and COX4 in intact mitochondria versus mitochondria depleted of the outer membrane. (d) Immunocytochemistry of cultured hippocampal neurons showing co-localization of HA-labeled ΔN-Bcl-xL and GFP-labeled ATP c-subunit shRNA. Red: HA; green: GFP; blue: Hoechst-stained nuclei. (e) % of co-transfected neurons/all transfected neurons. (f) Primary hippocampal neurons expressing empty vector plus scrambled GFP-labeled shRNA, empty vector plus GFP-labeled ATP c-subunit shRNA, ΔN-Bcl-xL plus GFP-labeled scrambled or ΔN-Bcl-xL plus ATP c-subunit shRNA stained with TMRM. Red: TMRM; green: GFP. (g) TMRM intensity (n=25-41 cells). Scale bar=10 μm. *P<0.05, ***P<0.001 and ****P<0.0001, one-way ANOVA