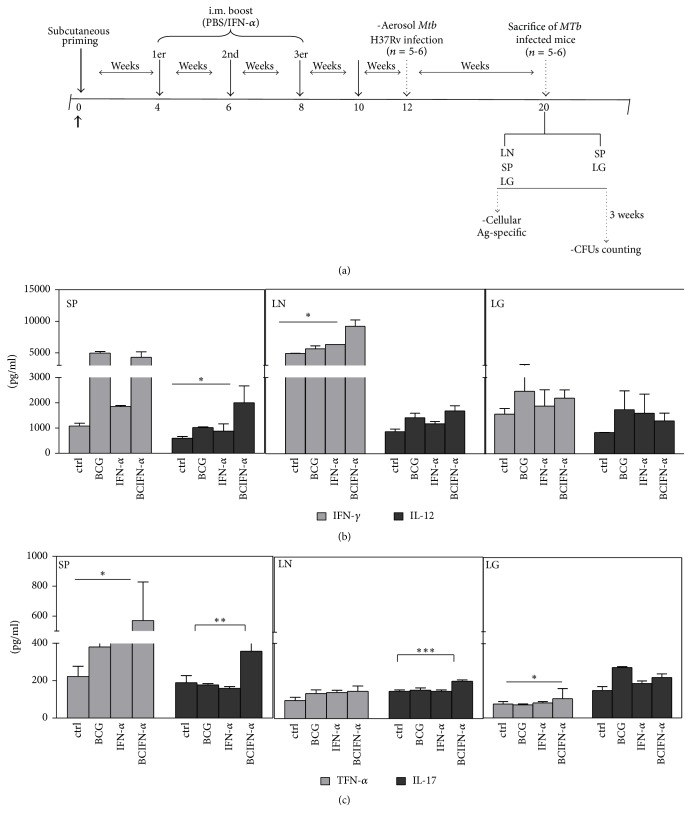
Figure 2.
(a) Schematic representation of the designed protocol used in this study. Seven- to eight-week-old adult BALB/c mice were primed with PBS (group a); 100 UI of IFN-α (group b); 5 × 105 CFUs of BCG Pasteur (group c); and 5 × 105 CFUs of BCG + 100 UI of IFN-α (group d). Four, six, and eight weeks after the priming, mice from groups a and c received PBS, while mice from groups b and d received IFN-α (100 UI), respectively. Two weeks after the third boost, mice were infected by aerosol route with a low dose (100 CFUs) of M. tuberculosis H37 Rv. Eight weeks after infection, mice were sacrificed to determine CFU counts in the lungs and spleen. (b-c) Cell culture of lymph node, spleen, and lung was stimulated in vitro with HBHA and cytokine production was measured by ELISA. Values are expressed in pg/ml and represent media ± SEM of samples tested in duplicate from each group of mice. Differences are significant at P < 0.05 with respect to control PBS immunized mice (∗) and with respect to BCG vaccination without boost (∗∗).