Figure 2.
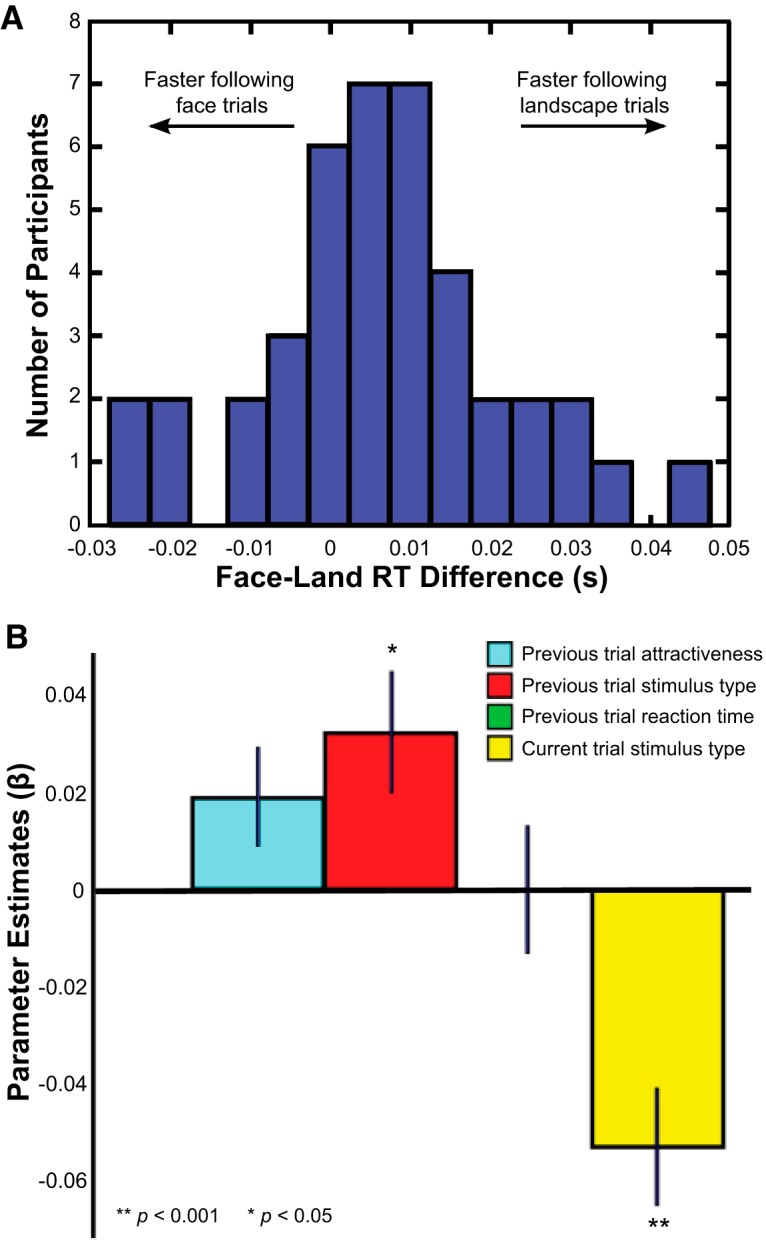
RTs are slower following face trials compared to landscape trials. A, Distribution of RT differences according to previous trial’s stimulus type, calculated by subtracting RTs following nonsocial trials from RTs following social trials. RTs on trials following social rewards were greater than those on trials following nonsocial rewards, indicating an effect of previous reward stimulus type on subsequent behavior. B, Average β weights (with SEM plotted) across subjects from a behavioral regression predicting current RT. We regressed current trial RT on a model including the following regressors: stimulus category (social or nonsocial) on previous trial, RT on previous trial, attractiveness rating of the previous trial’s reward, and stimulus category on current trial. Of these four regressors, current stimulus category most strongly predicted current RT; the negative β weight indicates that participants are faster to respond during a social trial compared to during a nonsocial trial. The next most predictive regressor was previous trial’s stimulus category; the positive β weight indicates that participants were slower to respond following social trials compared to following nonsocial trials. Neither previous trial’s RT nor previous trial’s reward attractiveness significantly predicted the current trial’s RT.
