FIG 7 .
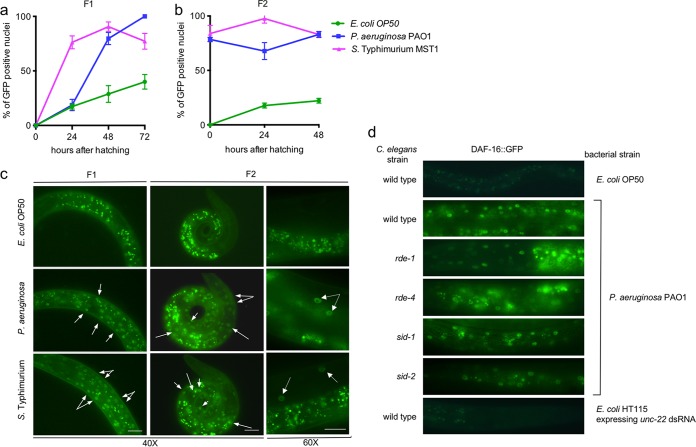
DAF-16 activation begins in the adult animals of the first generation exposed to pathogens. (a, b) Time course of DAF-16::GFP nuclear translocation in muIs61 F1 (a) and F2 (b) animals feeding on E. coli OP50, P. aeruginosa PAO1, and S. Typhimurium MST1. Points are average results for 90 animals from triplicates. Error bars indicate SEM of at least three biological replicas. (c) Photographs of nuclear expression of DAF-16 in the nuclei of muIs61 animals as adults in the F1 and young larvae in the F2 generation. Arrows indicate individual GFP expressing nuclei. (d) Nuclear DAF-16::GFP expression of RNAi mutant animals exposed to pathogenic bacteria. Photographs of wild-type and mutant animals expressing DAF-16::GFP after feeding on P. aeruginosa PAO1. As controls, wild-type animals were exposed to E. coli OP50 and E. coli HT115 expressing unc-22 dsRNA. Scale bars represent 30 μm.