Table 2. Scope of the catalytic enantioconvergent formal [1,3]-rearrangement with respect to propargylic substituents a .
| |||
| Entry | R′ | Yield b (%) | er c |
| 1 (4a) |
|
90 | 97.5 : 2.5 |
| 81 d | 97.5 : 2.5 d | ||
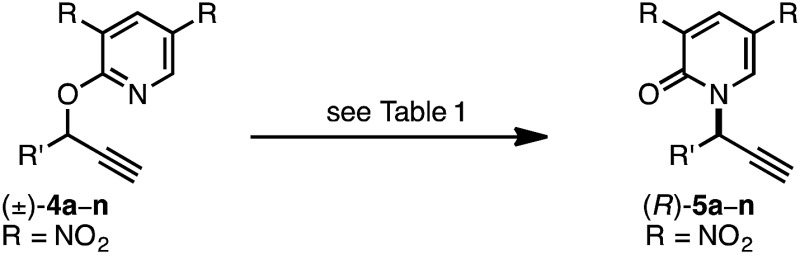
| 2 (4b) |

|
76 | 97 : 3 |
| 3 (4c) |
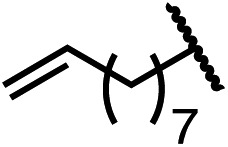
|
88 | 95.5 : 4.5 |
| 4 (4d) |
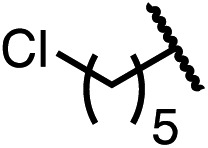
|
92 | 97 : 3 |
| 5 (4e) |
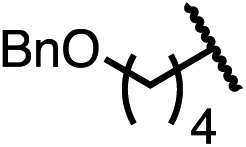
|
90 | 96.5 : 3.5 |
| 6 (4f) |
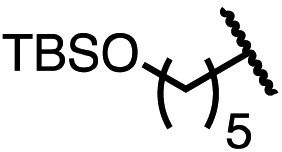
|
75 | 96.5 : 3.5 |
| 7 (4g) |
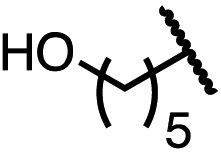
|
52 | 63 : 37 |
| 8 (4h) |
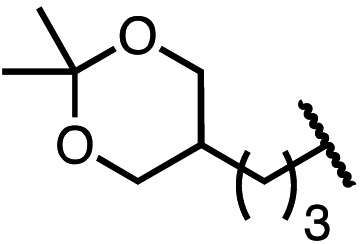
|
88 | 97 : 3 |
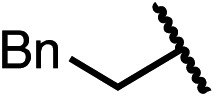
| 9 (4i) |
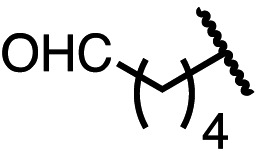
|
89 | 96.5 : 3.5 |
| 10 (4j) |
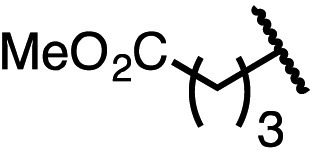
|
90 | 96 : 4 |
| 11 (4k) |
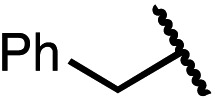
|
49 | 62 : 38 |
| 12 (4l) |
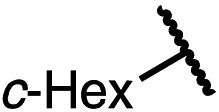
|
80 | 95.5 : 4.5 |
| 13 (4m) |

|
30 | 55 : 45 |
| 14 e (4n) |
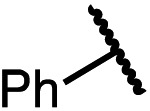
|
70 | 85 : 15 |
aAll data are the average of two experiments performed using 0.4 mmol substrate, unless otherwise stated.
bIsolated yields.
cDetermined by chiral stationary phase HPLC.
dPerformed using 5.0 mmol of substrate.
eThe Cahn–Ingold–Prelog terminology for product 5n denotes the (S)-configuration. Bn = benzyl; TBS = tert-butyldimethylsilyl; 1-Adam = 1-adamantyl.
