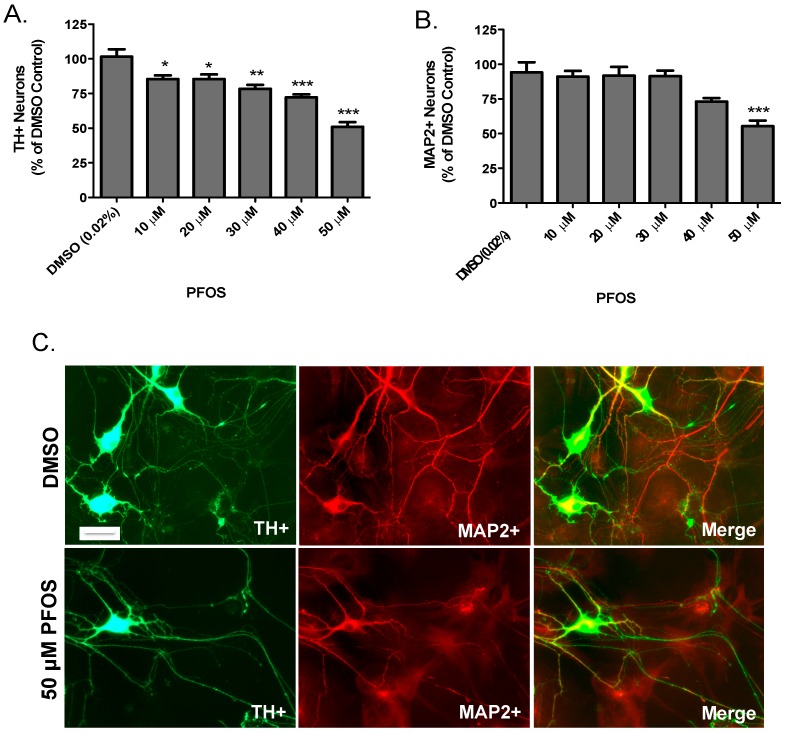
Figure 2.
Acute exposure to PFOS results in a preferential reduction in the number of primary cultured dopaminergic neurons. (A) Treatment with PFOS resulted in a significant reduction in the number of TH+ neurons, beginning at 10 μM; (B) treatment with PFOS did not elicit overt loss of non-dopaminergic neurons (MAP+), except at the highest concentration of PFOS (50 μM); and (C) representative images of TH+ and MAP2+ neurons following treatment with DMSO or 50 μM PFOS. Scale bar: 10 μm. Columns represent the percent change from DMSO control. Data represent the mean + SEM of 6 experimental replicates per treatment group performed over three separate experiments. * Values statistically significant from DMSO control (p < 0.05). ** Values statistically significant from DMSO control (p < 0.01). *** Values statistically significant from DMSO control (p < 0.001).