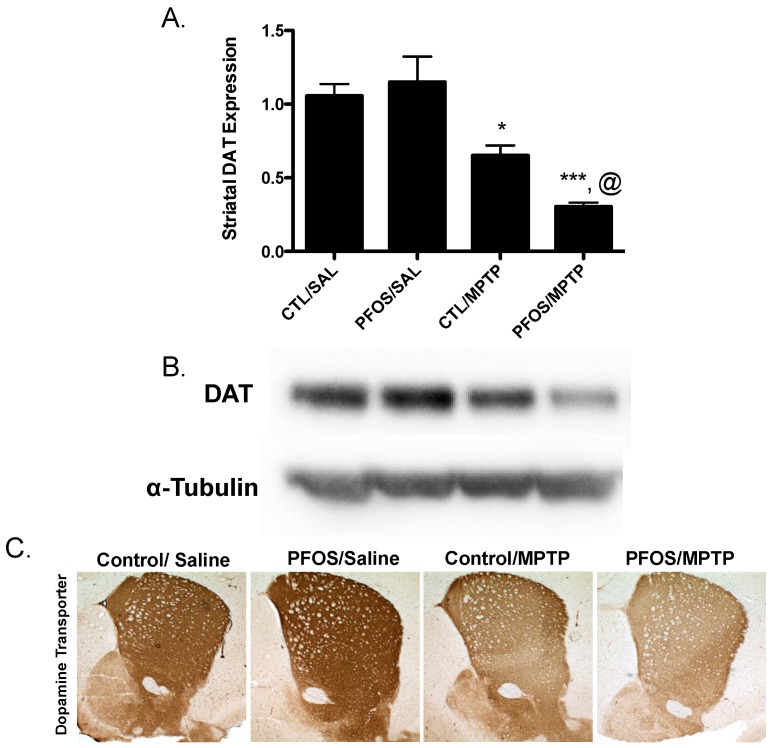
Figure 4.
Challenge with the dopamine neurotoxin, MPTP, causes significant reductions in DAT expression following PFOS treatment. An additional cohort of nine-week-old C57BL/6J male mice were exposed to 10 mg/kg PFOS for 14 days. One day following the last PFOS exposure, mice were injected with saline or 10 mg/kg MPTP at 7:00 a.m. and 7:00 p.m. and then allowed to sit for seven days before analysis. (A) Treatment with MPTP resulted in a significant reduction in the expression in striatal DAT in control animals that did not receive PFOS. Moreover, treatment with MPTP exacerbated reductions in striatal DAT in animals that had received PFOS prior to MPTP treatment; (B) and (C) are representative immunoblot and immunohistochemical processing, respectively, demonstrating the reductions in DAT expression in the striatum of treated animals. α-Tubulin was included to ensure even protein loading. Columns represent means of raw data + SEM (six mice per treatment group). * Values statistically significant from CTL/SAL (p < 0.05). *** Values statistically significant from PFOS/SAL (p < 0.001). @ Values statistically significant from CTL/MPTP (p < 0.01).