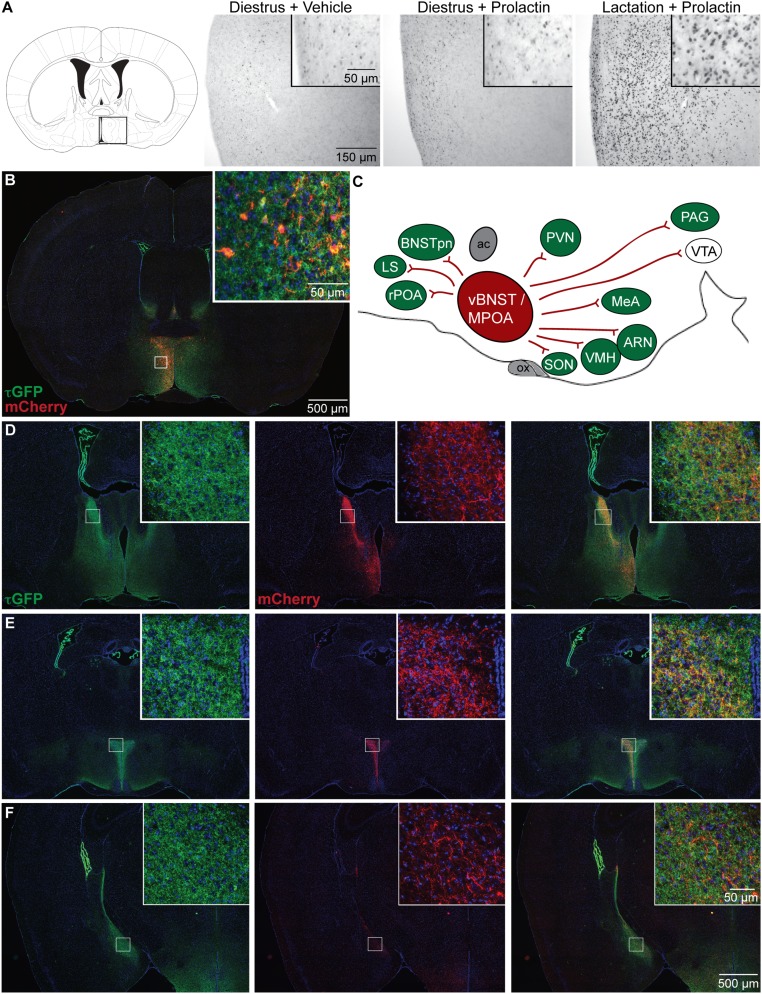
Fig. 1.
A prolactin-sensitive neural network centered on the medial preoptic area (MPOA). (A) Changes in prolactin-induced signal transduction in Prlr-expressing MPOA neurons. Photomicrographs show immunohistochemical labeling of pSTAT5 (black nuclear staining) after prolactin administration in diestrus nonlactating mice and day 7 lactating mice compared with vehicle-treated controls. Prolactin induces widespread and intensive pSTAT5 labeling in lactating mice but not in diestrus mice. (B–F) Distribution of projections from Prlr-expressing neurons in the MPOA. Prlr-iCre/eR26-τGFP mice received a unilateral injection of AAV5-EF1a-DIO-hChR2(H134R)-mCherry-WPRE-pA into the MPOA to drive Cre-dependent expression of mCherry specifically in the MPOA. Images were captured using a 10× objective using a Zeiss Axio Imager2 microscope with a motorized stage, with multiple images combined to form a composite image using the MozaiX module in the Axiovision software. (B) Site of the injection into the MPOA, with Prlr-expressing cells being labeled with τGFP (green) and a subset of Prlr-expressing neurons in the MPOA on one side expressing mCherry (red). (C) Schematic representation of mCherry-labeled projections from the MPOA in the sagittal plane, with regions containing Prlr-expressing cells colored in green and regions lacking Prlr-expressing cell bodies in white. ac, anterior commissure; ARN, arcuate nucleus; BNSTpn, bed nucleus of the stria terminalis principle nucleus; LS, lateral septum; MeA, medial amygdala; ox, optic chiasm; PAG, periaqueductal gray; PVN, paraventricular nucleus; rPOA, rostral preoptic area; SON, supraoptic nucleus; vBNST, ventral bed nucleus of the stria terminalis; VTA, ventral tegmental area. (D–F) Representative sections illustrating the distribution of τGFP labeling showing Prlr expression (green), mCherry-positive projections of MPOA prolactin receptor-expressing cells (red), and the composite images through the forebrain (Figs. S1 and S2 and Table S1).