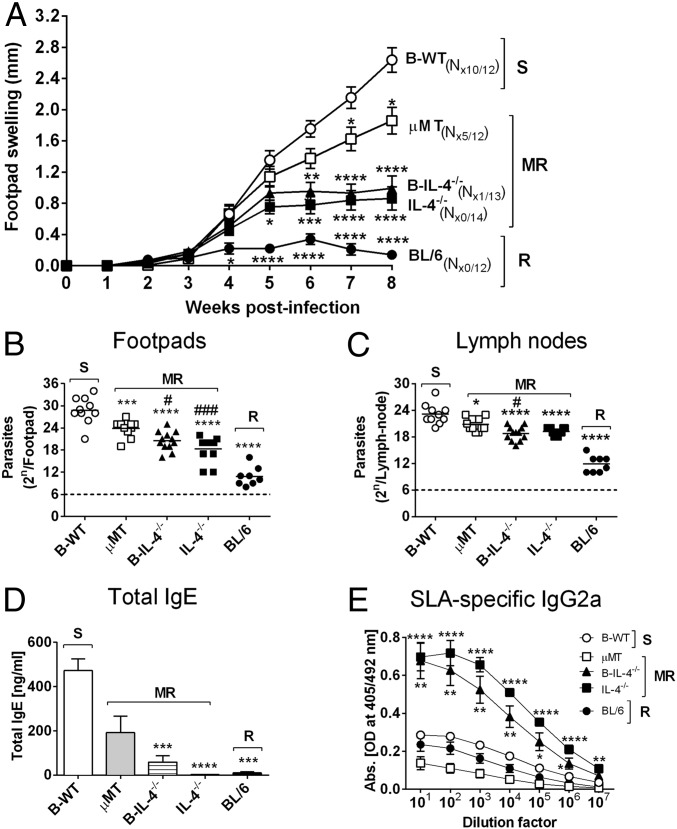
Fig. 4.
IL-4–producing B cells influence susceptibility to L. major infection in BALB/c mice. (A) Respective chimeric mice (Fig. S8) were infected with 2 × 106 L. major LV39 (MRHO/SV/59/P) promastigote parasites into the hind footpad, and footpad swelling was measured weekly. (B and C) Parasite burden was determined by limiting dilution of homogenized footpads (B) and draining LNs (C) at 8 wk after infection. (D and E) Total IgE (D) and SLA-specific IgG2a (E) antibody isotype production was measured from infected sera by ELISA. Data represent a pool of two independent experiments (n = 12–14 mice per group). Statistical analysis was performed defining differences to B-WT mice (*P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001, ****P ≤ 0.0001) and µMT as significant (#P ≤ 0.05, ###P ≤ 0.001). N#/12–14, where # represents number of mice in a group of 12–14 showing necrosis/ulceration. MR, moderately resistant; R, resistant; S, susceptible.