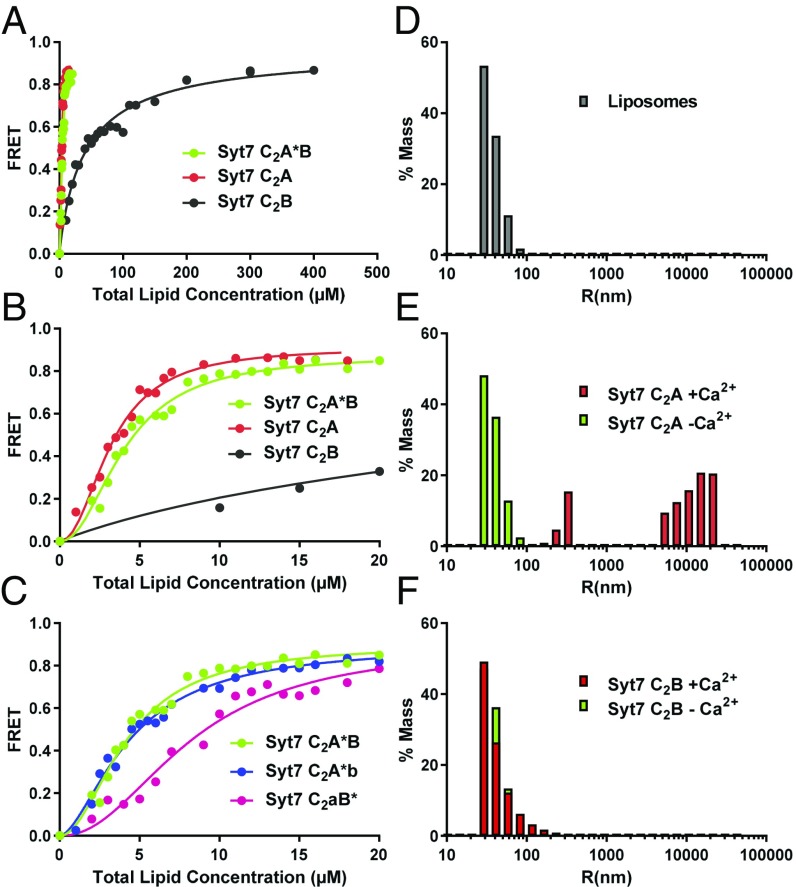
Fig. 4.
The Syt7 C2A domain dominates binding of Syt7 to membranes and clusters liposomes. (A) Titrations of 20 nM Syt7 C2A domain, C2B domain and C2A*B fragment (the * in C2A*B denotes that the fluorescent probe is attached to C260 of the C2A domain) with liposomes lacking PIP2 in the presence of 1 mM Ca2+. Binding was monitored from the FRET developed between a donor BODIPY-FL probe attached to the proteins and a rhodamine acceptor present in the liposomes. Each point represents the average of at least three measurements performed with different liposome preparations. (B) The same titrations shown in A but changing the x axis to better show the points of the titrations obtained at low liposome concentrations. (C) Liposome titrations of 20 nM WT Syt7 C2AB fragment and mutant fragments where the Ca2+-binding sites of the C2A domain (C2aB*) or C2B domain (C2A*b) were disrupted with D225A,D227A,D233A or D357A,D359A mutations. All of the data in A–C were fit to a Hill function. (D–F) Distribution of particle size measured by DLS on samples containing liposomes alone (D) or liposomes in the presence of the Syt7 C2A domain (E) or Syt7 C2B domain (F). In E and F, the diagrams show superpositions of data obtained in the absence (green bars) or presence (red bars) of Ca2+.